How to spot fake documents: Ultimate guide


How do you tell if a document is real or fake?
In 2026, knowing how to spot fake documents (and how document fraud detection solutions expose them) goes a long way toward fighting fraud in your business.
Document fraud cases are increasing every day, especially among documents used for fintech onboarding and verification purposes. Being able to detect these forgeries is more important than ever.
In this guide, we will outline the most commonly faked documents, how to spot them, and link to complete summaries on everything to look for when checking these documents for fraud.
If you’d like to know how fraudsters are creating all these fake documents, check out our “Types of fraud” blog to learn more about their tactics.
How to spot a fake proof of address
Proof of address can present a problem for traditional fraud detection: fake utility bills, manipulated bank statements, or fake Social Security awards are just a few examples of common forgeries we've come across.
Keeping up to date with every possible issuing authority simply isn't possible, especially for multinational businesses dealing with customers all over the world. But the documents that can be used as proof of address are also usually straightforward, and so are frequently made from scratch by unskilled forgers or template farms.
For instance, some proof of address fake docs appear frequently, such as documents from major energy companies and large banks.
However, the frequency of these fakes might lead to their eventual downfall. It's easy to verify incoming documents using previous examples. Logo detection can flag out-of-date designs or page layouts inconsistencies and machine learning pattern detection can eventually spot overuse of the same fake template (i.e., all submissions have the same rip in the paper or similar lighting effects).
For documents that are less commonly submitted from lesser known authorities, minor qualities that can go unnoticed by humans (like copy-pasted letters or inconsistent image qualities) can certainly point to a fraudulent document.
How to spot a fake utility bill
Utility bills are service provider-issued documents that verify a person’s or business’s connection to a specific physical address. They detail usage and payments for electricity, gas, water, or internet, and typically include billing dates, account numbers, and meter readings.
Because they’re widely accepted as proof of address, utility bills play a key role in KYC checks, loan approvals, lease agreements, and government registrations. That makes them a popular tool for fraudsters looking to fake residency, disguise shell companies, or slip past identity checks.
Fake utility bills often rely on cloned templates, copy-pasted branding, or mismatched region-specific details. Fraudsters also exploit editable PDFs or AI tools to recreate usage graphs and customer data fields—sometimes with alarming precision.
Effective fraud detection software goes beyond reading the document. It analyzes file structure, layout patterns, and metadata to confirm whether the bill came from a real provider and whether any modifications occurred before submission. If those structural fingerprints don’t line up, there’s a good chance the utility bill is fake.
These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake lease
Fake leases are a common way for applicants to invent a phony address or fabricate proof of rental income for a loan application. Scammers can easily grab a standard lease template online and populate it with convincing, but false, details, creating a document that easily fools a human reviewer.
The key to catching these forgeries isn't to play detective and track down the supposed landlord. It's about finding the digital evidence of tampering within the file itself, like spotting where a signature was crudely pasted in or identifying that the tenant's name was typed in a different font from the rest of the text.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot fake tax documents
Tax documents are critical documents used across industries to verify income, assess financial integrity, and ensure regulatory compliance. Given their detailed financial information, they are often required for loan applications, government benefits, and background checks.
These counterfeit documents often exhibit telltale signs such as inconsistent formatting, outdated templates, or mismatched metadata. For instance, fraudsters might use obsolete forms or combine elements from various documents, leading to discrepancies in layout or information.
Detecting such subtle inconsistencies requires advanced analysis beyond manual inspection.
AI-powered verification tools, like those offered by Resistant AI, can scrutinize these documents for over 500 indicators of fraud, including structural inconsistencies and metadata irregularities, ensuring the authenticity of tax returns and safeguarding against financial deception.
These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake W2
W2 forms come into play during tax season as well as when lenders and government services need to verify proof of employment and other personal details.
Fraudsters often present fake W2s to inflate their income, resulting in the ability to be approved for loans or interest rates they aren't qualified for or which they never intend to pay back at all.
Fake W2s and other very common standardized fake docs might seem like easy targets for forgery and manipulation, but their consistency actually helps catch underhanded dealings.
If certain fields don't align with the rest of the form or non-standard fonts appear, there's a good chance that you're dealing with a fake form.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake P60 form
Fake P60 forms are a go-to for applicants trying to commit loan or mortgage fraud by inflating their income. The doctored documents can look perfect at a glance, with legitimate employer details but falsified salary and tax figures that are almost impossible for a human to spot.
The key to catching these lies in analyzing the file's digital DNA rather than trying to manually verify the numbers with HMRC. Specialized software can instantly spot the microscopic inconsistencies that prove the 'total pay' or 'tax deducted' fields have been digitally manipulated, exposing the fraud on the spot.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake receipt
Receipts are merchant-issued documents that serve as proof of a financial transaction, listing items purchased, prices, taxes, and payment methods. They’re used in expense reporting, reimbursements, audits, tax deductions, and returns—and are often required to validate financial claims across business and government workflows.
Because they’re easy to fabricate and widely accepted, fake receipts are a favorite tool for inflating expenses, committing reimbursement fraud, or covering up phantom purchases. Fraudsters manipulate line items, swap logos, or clone layouts using editing tools and AI-powered generators.
Detecting fake receipts requires more than checking the math. Reliable fraud detection software inspects file metadata, layout structure, and merchant identifiers.
It can flag discrepancies like pixelated barcodes, inconsistent timestamps, or receipts created after the listed purchase date. If those signals don’t add up, the receipt probably isn’t real.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot fake insurance documents
Insurance documents supports claims, verifying proof of travel, purchase, and that an incident occurred.
How to spot a fake NCD letter
Fake no claim discount (NCD) letters are vital for auto insurers and intermediaries to provide competitive rates during policy onboarding and insurer switching.
These letters prove a customer’s claims-free history. But NCD letters are often shared as simple PDFs or scans — making them prime targets for modern forgery tactics like format hopping and templated fakes.
Without reliable ways to spot these fake documents, insurers risk mispricing policies, skewing risk models, and ultimately absorbing the financial impact of undetected fraud.
From structural inconsistencies and metadata red flags to increasingly sophisticated automated manipulation, spotting NCD fraud is at the frontline of preventing risky customers from getting unfair rates.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake flight ticket
Scammers easily create fake flight tickets to cheat visa systems with bogus "proof of onward travel" or to file inflated business expense reports. These forgeries often use convincing templates where key details like the PNR number, flight details, and QR codes appear legitimate, making them impossible to verify manually.
A true forensic analysis ignores that data and instead confirms if the airline logo is a low-quality pasted image or if the QR code was digitally inserted after the fact. This AI-driven approach looks for these structural signs of fabrication, proving the document wasn't generated by a legitimate airline booking system.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake travel itinerary.
Travel itineraries are essential documents used to verify travel plans for purposes such as visa applications, corporate expense reimbursements, and insurance claims. They typically include details like booking reference numbers, traveler names, flight and accommodation information, travel dates, and issuing entities.
To detect fraud in travel itineraries, it's important to scrutinize inconsistencies in formatting, verify booking references with official sources, and examine metadata for signs of tampering. AI-powered tools, like those offered by Resistant AI, can analyze documents for over 500 indicators of fraud, including structural anomalies and metadata discrepancies, providing a robust defense against sophisticated forgery attempts.
These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake hotel booking
Hotel bookings are a common target for fraud, used to file fake travel insurance claims for "cancelled" trips or to invent multi-night stays for expense reports. Fraudsters leverage convincing templates complete with real hotel logos and addresses, making it nearly impossible for a human reviewer to spot a fake based on visual inspection alone.
Instead of manually trying to confirm a booking reference number, forensic analysis can instantly prove the document is a fabrication. This AI-powered approach can tell if a hotel's logo was poorly pasted onto the page or determine if the room rate and dates were digitally manipulated long after the original confirmation was issued.
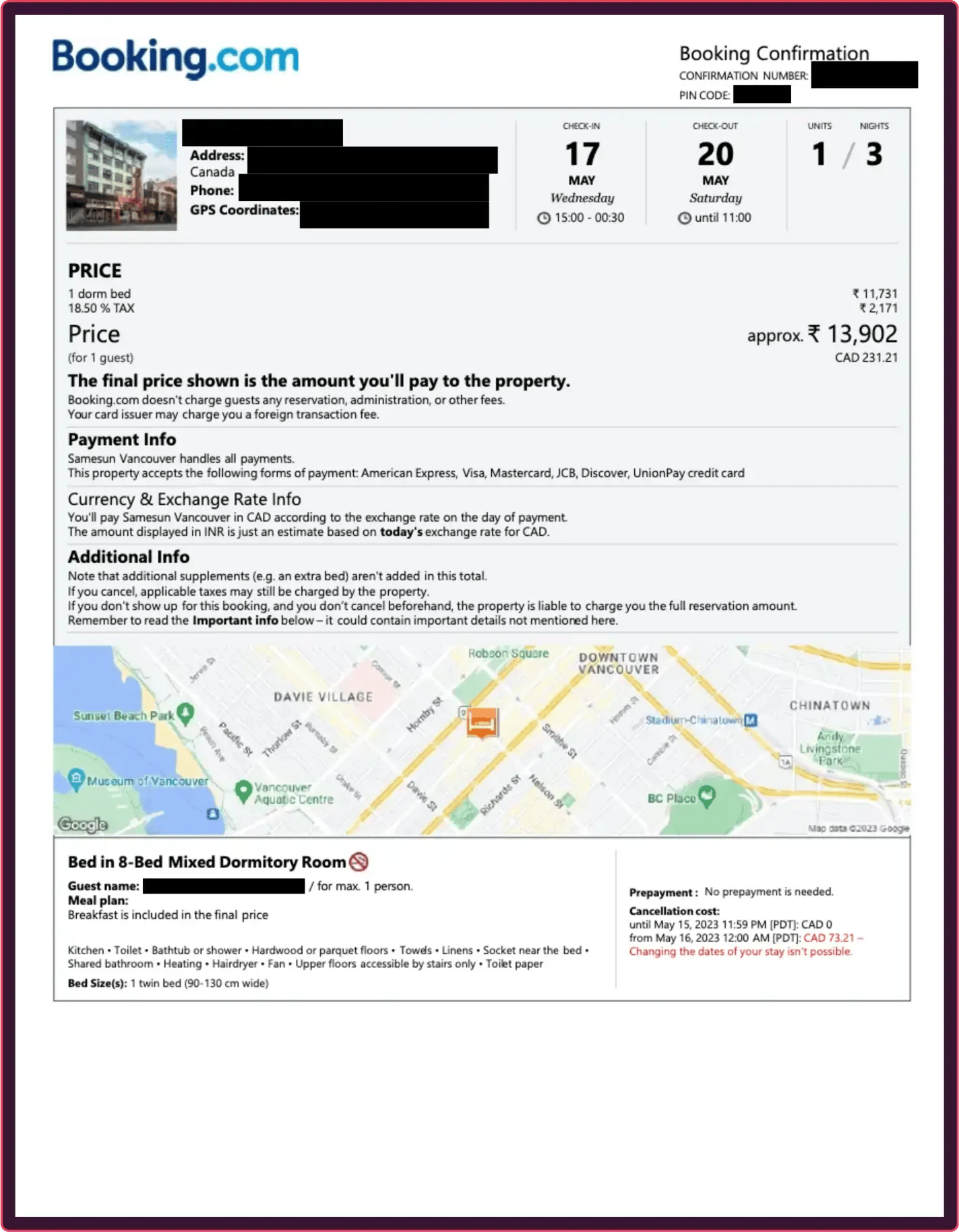
These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake police report
Police reports are a key tool for insurance fraud, allowing criminals to falsely claim a car was stolen or property was damaged. These forgeries are built from convincing templates featuring official-looking crests and case numbers, making them nearly impossible to disprove through visual inspection.
Rather than trying to manually verify a case number, a forensic analysis can instantly prove the document itself is a fabrication. This AI-powered approach detects if a police department’s crest is a pasted image or reveals when the text describing the incident has been digitally altered.
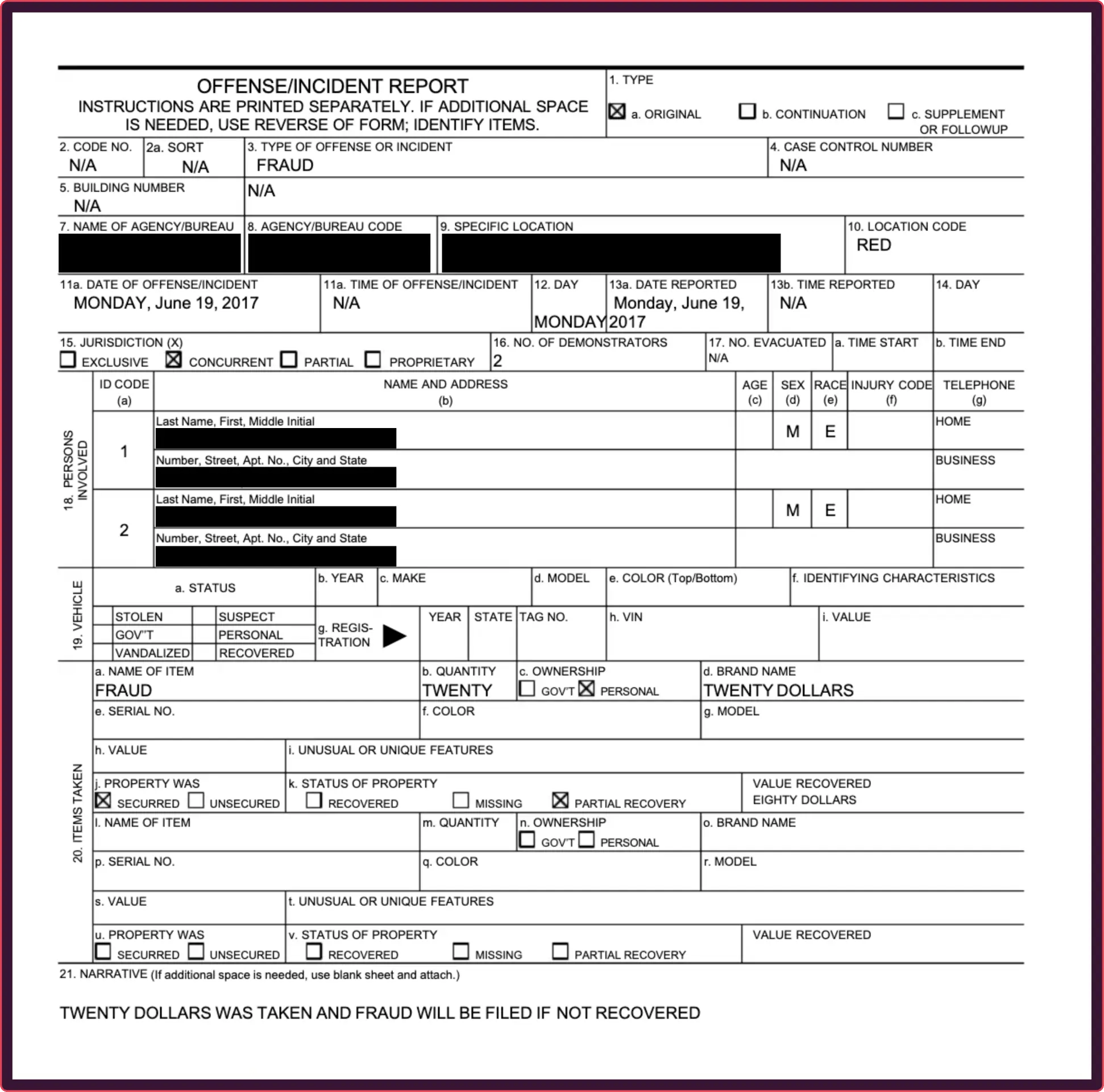
These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot fake merchant onboarding materials
Merchant onboarding or know your business (KYB) can carry even higher stakes than KYC onboarding processes:
-
Penalties for doing business with inappropriate figures can be higher.
-
More overlapping jurisdictions might come into play.
-
Losses for the SME lenders themselves are often much larger.
Fake merchant onboarding materials like certificates of incorporation or business licenses can have the added complications. They contain information from many localities and obscure institutions, sometimes in languages and government structures most review teams aren't well versed in.
However, uncovering what is and isn't valid doesn't always require assembling expensive teams of specialists or reaching out to overloaded civil servants.
Again, a forensic look at the documents a business provides can reject many instances of attempted fraud right away. Completely language and nationality agnostic, fraudulent merchant onboarding materials can be spotted via:
-
Variations in image qualities
-
Font inconsistencies
-
Reused images properties
Additionally, attributes unique to business documents such as digitally added official stamps or notarizations can offer even more opportunities to find fake documentation attempts.
How to spot fake articles of association
Articles of association are foundational legal documents that define a company's internal governance, outlining roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes. They are crucial for verifying corporate legitimacy, especially in contexts like banking, compliance, and mergers. However, fraudsters often forge these documents to create shell companies or impersonate legitimate businesses, facilitating illicit activities.
Detecting fake articles of association involves scrutinizing for inconsistencies such as mismatched formatting, incorrect company numbers, or discrepancies with official registries. Advanced AI-powered verification tools, like those offered by Resistant AI, can analyze these documents for subtle anomalies and metadata discrepancies, ensuring authenticity and protecting against sophisticated fraud schemes.
These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake certificate of incorporation
A certificate of incorporation is an official document that proves a company’s legal existence and is often required for onboarding, due diligence, or compliance checks.
Fraudsters target it because it's commonly accepted at face value and easy to replicate using templates or editing tools.
For organizations, trusting a fake certificate can mean onboarding shell companies, violating regulations, or enabling financial crime.
Detecting these fakes requires more than manual review — AI-powered document forensics can analyze layout inconsistencies, metadata, and behavioral patterns that signal tampering.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake business license
A business license is an official government-issued document that grants a company the authority to operate in a specific location or industry.
Fraudsters forge them to bypass regulatory scrutiny, appear legitimate to partners, or gain access to financial services under false pretenses.
Organizations rely on valid business licenses for compliance, vendor verification, and fraud prevention during customer or partner onboarding.
AI-based document forensics can detect subtle signs of forgery — such as reused templates, altered registration numbers, or mismatched jurisdiction data — that manual checks often miss.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake EIN verification letter
Fake EIN verification letters are used to establish legitimacy for shell companies in synthetic identity fraud schemes, enabling criminals to secure business loans they never intend to repay. These documents, like the official CP 575 form, are simple in design and easily forged from templates, making them nearly impossible to flag through manual review.
A forensic analysis bypasses the need to manually contact the IRS by instantly proving the document's structure is fraudulent. This AI-driven approach can detect if the official IRS letterhead is a low-quality pasted image or identify text inconsistencies where a fake business name was digitally inserted.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot fake KYC documents
Spotting fake KYC documents spans everything from low-effort amateur edits to highly sophisticated, professional attacks designed to pass automated and manual reviews alike.
ID cards, marriage certificates, birth certificates, and more attract different fraud techniques, levels of sophistication, and risk profiles.
In the sections below, we break down how fake KYC documents are created, what red flags actually matter, and how fraud tactics differ by document type.
How to spot fake marriage certificates
Fake marriage certificates are often used to validate sham relationships in immigration, benefits, or identity fraud schemes, enabling fraudsters to unlock visas, financial advantages, or eligibility-based services they aren’t legitimately entitled to. Unlike highly secured civil records, many marriage certificates follow simple layouts with basic fields, making them easy to replicate using template farms or generative AI tools that bypass casual manual checks.
Forensic document analysis eliminates the need to contact registrars or rely on visual familiarity by exposing structural and metadata anomalies that never occur in authentic records. By inspecting text layers, spatial relationships, and digital fingerprints, AI-powered systems can detect tell-tale signs such as inconsistent formatting, misaligned seals, improbable personal data, and metadata indicating consumer editing tools — red flags invisible to manual review.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot fake birth certificates
Fake birth certificates are a foundational tool in identity and synthetic fraud because they’re treated as one of the most authoritative “breeder documents.”
Unlike highly secured IDs, birth certificates come in thousands of jurisdiction-specific formats with minimal surface security, making template-based fakes and generative AI creations easy to produce and hard to catch through visual review alone.
Forensic, AI-driven analysis eliminates guesswork by inspecting the document’s internal structure, metadata, and construction.
.png?width=875&height=1212&name=birth%20cert%20demo%20doc%20(1).png)
These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake ID
Since they are the foundation of most know your customer (KYC) onboarding processes, it's crucial to be able to detect fake ID cards like driver's licenses or passports.
One of the primary ways fraudsters manipulate IDs is through image doctoring, altering the photo, name, or other details on the ID itself.
This can be quite crude: it's often evident when words have been inserted or an all new photo has been imported into the image file.
These modifications usually leave traces in the image metadata as well as in image attributes that don't match across different portions of the card.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
Stolen, unaltered IDs being reused or IDs that have undergone pre-digital modification, meanwhile, can still present problems for more traditional fraud detection software.
However, these can be detected by noting image similarities across a collection of images. A recurring background is usually a dead giveaway: the same person taking the same type of photos in the same place.
Even if the fraudster is clever and uses different backgrounds, lighting, effects, etc, if they match characteristics seen elsewhere, or attributes of the device that has uploaded the photo, the fraudster can be caught red-handed.
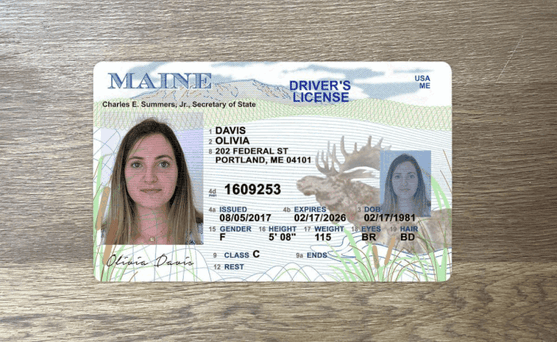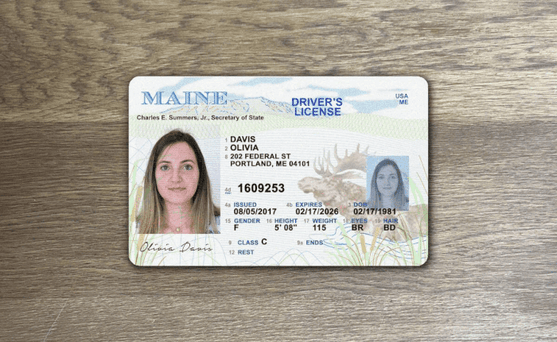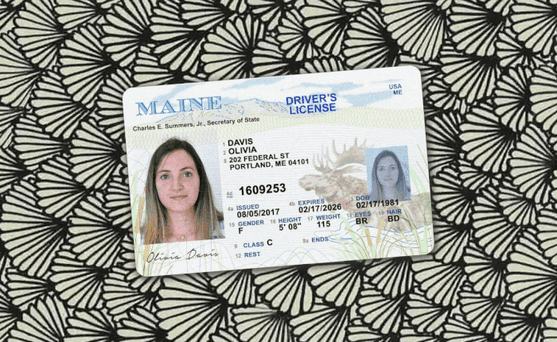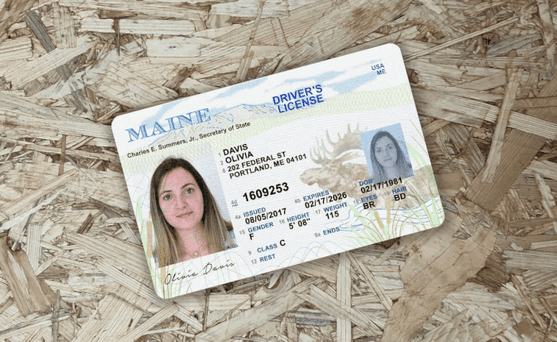
These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake proof of income
Proof of income presents a similar challenge for traditional fraud detection: fake pay stubs, bank statements, and invoices are just a few of the common forgeries we encounter.
Keeping up to date with every employer, payroll provider, or tax authority worldwide isn’t feasible. At the same time, proof of income documents tend to be an attractive targets for template farms and opportunistic fraudsters who generate them from scratch.
Certain fake proof of income documents appear again and again — for example, pay stubs generated online are becoming more common in our data sets.
Read on to learn about specific income documents and how to spot when they're faked.
How to spot a fake pay stub
Pay stubs are employer-provided documents that outline an employee’s earnings and deductions for a specific pay period. They typically include: gross wages, taxes withheld, benefits contributions, and net pay.
Pay stubs maintain transparent payroll records, help employees understand their compensation, and ensure compliance with tax and labor regulations.
Fraudsters create fake pay stubs to deceive lenders, landlords, or government agencies by inflating income or fabricating employment. They're often used to secure loans, rent properties, or qualify for benefits under false pretenses.
Spotting fake pay stubs and tax forms also comes down to metadata. Businesses both large and small typically rely on accounting software to generate these all-important records, leaving specific markers.
Quality fraud detection software uses these to note whether a bookkeeping program was the originator of a given file and whether any alterations have occurred between the time of output and the time the document is submitted.
If one of these checks turns up something unexpected, a fake pay stub or a fake tax document is very possible.
It's important to note that metadata inconsistencies alone aren't proof of a fraudulent document; cross-checks with other analyses (in our case over 500 different detectors) usually tabulate a long list of evidence that indicates a high likelihood of document fraud.
These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake bank statement
Bank statements are important tools for confirming proof of funds, proof of income, and proof of address, especially for online lenders aiming to carry out the underwriting process.
Skilled fraudsters will probably skip outright fake docs forgery, choosing instead to edit PDF versions of bank account statements—these can easily be found online or downloaded from an email or banking app.
While the altered end product may be convincing to the human eye, this approach leaves an obvious technological trail that the file has undergone unauthorized changes.
In addition to the logo detection and image attributes mentioned above, these attempts at creating fake bank statements also leave "fingerprints" in the metadata of the files themselves.
Anything from timestamps to the software used to create the document (as well as dozens of other small details) can distinguish between a real bank statement and an illegitimate one.
Of course, these red flags of fraud require forensic analysis of the file in question.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake invoice
An invoice is a formal document issued by a seller to a buyer, detailing goods or services provided, their quantities, prices, and payment terms. Companies use invoices to request payment, maintain financial records, and ensure accurate accounting. They are essential for tracking sales, managing cash flow, and fulfilling tax obligations.
Fraudsters manipulate invoices to deceive businesses and siphon funds. Common tactics include:
-
-
Altering invoice details using editing tools.
-
Creating fake vendors with fabricated contact and payment information.
-
Compromising vendor emails to redirect payments.
-
Red flags of invoice fraud include: discrepancies between purchase orders and invoices, unusual pricing that doesn't align with market rates, missing product identifiers like serial numbers, and inconsistencies in contact details or payment information.
To detect invoice fraud, companies should implement thorough verification processes, cross-check invoice details with purchase orders, and remain vigilant for any anomalies or unexpected changes in vendor information.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot fake trade finance documents
Trade finance document verification introduces a complex and high-stakes dimension to fraud prevention:
-
Individual transaction values can reach millions of dollars.
-
Multiple independent parties (buyers, sellers, banks, insurers) all rely on the same set of documents.
-
The inherent cross-border nature creates a tangle of jurisdictions and regulations.
Fraudulent documents like Bills of Lading, Certificates of Origin, or commercial invoices present a critical challenge. A single, well-executed forgery in this chain—such as a fake Bill of Lading—can be enough to release millions in funds for goods that don't exist or have already been sold.
However, ensuring the authenticity of this complex paper trail doesn't have to rely on a slow-moving, manual process of contacting international shipping lines, customs agents, and overseas banks.
How to spot a fake bill of lading
A bill of lading is a shipping document issued by a carrier to confirm that goods have been received for transport. It serves three key functions: it’s a receipt for the cargo, a contract of carriage between shipper and carrier, and (when negotiable) a document of title that determines who legally owns the goods.
For verification purposes, bills of lading confirm that a shipment exists, that it was handed over to a legitimate carrier, and that the listed parties and shipping terms align with what was agreed. This makes them essential for preventing cargo fraud, validating ownership, and supporting trade finance transactions.
Fake bills of lading are used to secure loans, redirect cargo, or sell goods that don’t exist. Because these documents move between multiple parties across international borders, fraud can go unnoticed until it’s too late.
Look for inconsistencies in layout, duplicate document numbers, unrealistic shipment routes, and file metadata that doesn’t match the issue date. AI-based tools can flag structural anomalies and repeated fraud patterns that human reviewers are likely to miss.
These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake export declaration
Export declarations are increasingly targeted in international trade fraud, used to fabricate the illusion of legitimate cross-border shipments. Criminals manipulate MRNs, alter HS codes, or generate entirely synthetic declarations to secure financing, evade sanctions, or claim tax rebates for goods that never moved.
Instead of relying on slow, uncertain checks across foreign customs systems, modern verification tools can analyze the declaration file itself for signs of digital tampering. This approach exposes fraud by revealing inconsistencies in the document’s structure, showing whether MRNs were reused across templates, or detecting if key customs data was inserted into a forged layout.
.png?width=1033&height=1337&name=export%20declaration%20demo%20doc%20(1).png)
These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake letter of credit
Letters of credit are a classic tool for fraud, used to trick exporters into shipping goods with no real guarantee of payment. Fraudsters impersonate legitimate, well-known banks on these documents, making it incredibly difficult for a seller to spot the fake before the cargo is already gone.
Rather than the impossible task of calling an overseas bank to confirm an L/C's validity, modern tools can analyze the document file itself for signs of digital forgery. This approach exposes the scam by revealing if the bank's letterhead was simply copy-pasted or if the payment terms were altered within a generic template.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake certificate of insurance
Certificates of insurance are one of the most commonly forged documents in contractor onboarding and cargo financing. Fraudsters edit policy numbers, inflate liability limits, or fabricate entire certificates to appear compliant, leaving businesses exposed to uninsured losses the moment something goes wrong.
Instead of chasing brokers for confirmation or trying to judge a COI by its layout alone, modern tools can analyze the file itself for structural red flags. This approach reveals whether coverage details were edited, signatures were pasted in, or the entire certificate was rebuilt from a generic template (long before your team approves an uninsured partner).

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
How to spot a fake certificate of origin
Certificates of origin are a common target in trade fraud, used to falsely qualify goods for preferential tariffs or to disguise shipments originating from restricted regions. Fraudsters alter country-of-origin fields, reuse old certificates, or fabricate chamber-issued documents to make non-compliant goods appear eligible for import.
Rather than relying on slow chamber verification or manually comparing stamps and signatures, modern tools can analyze the document file itself for signs of digital forgery. This approach uncovers fraud by detecting tampered seals, inconsistencies in layout or numbering, and evidence that key origin details were copied into a forged template.

These documents are not real, but recreations meant to demonstrate the fraud techniques described for illustrative purposes only.
Threat intel: Template data about fake document availability
Our Threat Intelligence Unit collects data about template farms which make and distribute fake document templates for fraudulent purposes.
Below, you'll find an infographic containing data about all the fake document templates we've found: their availability, their distributors, and how much it costs to buy one.

Find more information about the threat these farms pose in our threat intel blog and webinar content.
How to verify a document's authenticity?
There are two ways to verify documents' authenticity: manual reviews or using an AI-powered fake document checker.
With the rise of template farms (e.g., Doc Juicer), online editing tools, and advanced defrauding techniques, manual reviews are becoming less reliable.
The human eye struggles to detect subtle changes in metadata, formatting, and fonts, making AI-powered solutions more effective in detection fraud.
Conduct manual reviews
For manual reviews of documents, identifying signs of forgery is crucial for verifying the authenticity of documents. Here are some general tips for all documents:
-
-
Cross check with official registries and fraud databases.
-
Validate document contents with third-party information.
-
Scan publicly available information about the applicant or company.
-
Assess the contents to see if they make sense (i.e., everything adds up and isn't an outlier for that specific document/industry)
-
Use AI and machine learning
One of the best ways to verify the authenticity of a document is by using document and language-agnostic software: a one-size-fits-all fake document checker.
This approach preserves customer privacy while accurately detecting signs of forgery and falsification — regardless of document type.
Conclusion
Fraud is rarely a single bad PDF. Criminals assemble believable narratives and complete onboarding packages (fake IDs paired with forged leases, doctored pay stubs, and cloned utility bills) so a lone document check looks confident while the whole package is a lie. Catching that orchestration requires looking across files, not just at one page or document type in isolation.
Resistant documents does exactly that with any document type. Its structural analysis inspects how each file was built (not what it says), while cross-document intelligence finds repeated templates, reused assets, and linked anomalies across submissions.
The system flags GenAI-style artifacts, preserves privacy by avoiding PII extraction, and adapts detection thresholds to your risk profile so you stop fraud without slowing real customers.
The result is practical: fewer manual reviews, faster onboarding, and evidence you can defend in audits and disputes. See the links, patterns, and proof for yourself — scroll down to book a demo.