Receipts aren’t immune to forgery.
AI-enhanced editing tools and low-cost document template repositories have made it easier than ever to fabricate financial records and making fake receipts is a top target.
And this problem isn't disappearing in 2026. In February of this year, an Irish man charged with using fake receipts to obtain cash nearly escaped custody (if it wasn't for Storm Chandra).
From expense reports to tax deductions, these documents are trusted as proof of payment across industries. Fraudsters looking to manipulate spending data, exaggerate reimbursements, or invent transactions love using fake receipts because of their unstandardized formatting.
With the right tools, a scammer can fabricate store logos, replicate layout structures, and even mimic regional tax calculations with disturbing precision.
Whether you're validating a vendor transaction or reviewing employee expense claims, the ability to spot fake receipts has never been more critical.
Read on to learn what a receipt is, how they’re being forged, how to identify a fake receipt, and how AI-powered verification solutions can help spot them automatically.
Check out our “How to spot fake documents” blog to learn about more common document forgeries.
What is a receipt?
A receipt is a commercial document issued to confirm a financial transaction between a buyer and a seller. It serves as formal evidence that goods or services were paid for, detailing the amount, date, items involved, and point of sale. While receipts can be physical or digital, most share a consistent layout and a set of verifiable fields.
Receipts typically contain the following information:
-
Merchant name and contact information. Identifies the issuing business and its registered address, phone number, or tax ID.
-
Transaction date and time. Establishes when the payment occurred and timestamps the sale.
-
Line-item breakdown. Lists each purchased product or service, quantity, unit price, and subtotal.
-
Payment method and total amount. Confirms whether the transaction was completed via card, cash, or other means, including tax and discounts.
-
Reference numbers and identifiers. Includes order numbers, cashier IDs, terminal numbers, or transaction codes for traceability.
Receipts are primarily used to validate that a payment was made for specific items or services under a defined total.

An example of a receipt for illustrative purposes only
Why are receipts important?
Receipts are a foundational part of modern financial systems. They serve as proof-of-purchase for individuals and a key compliance artifact for businesses. When it comes to accounting, audits, reimbursement, and tax reporting, receipts provide necessary transparency and verification.
Here’s how receipts are used for document verification across specific industries:
-
Corporate finance. Used to substantiate employee reimbursements and track departmental spending across company accounts.
-
Retail & eCommerce. Customers rely on receipts for returns, warranty claims, and product disputes; businesses use them for inventory control.
-
Healthcare. Insurance providers and patients require itemized receipts for reimbursement claims, co-pays, or tax deductions on medical expenses.
-
Government & public sector. Agencies audit receipts to validate how allocated budgets are spent and ensure public funds aren’t misused.
-
Travel / Travel Insurance. Receipts are required to file travel insurance claims, verify travel-related expenses, and support reimbursement for trip cancellations, delays, or lost baggage.
Receipts are favored because they’re time-stamped, itemized, and widely accepted, but those same traits make them ripe for falsification.
If you’d like to know how fraudsters are creating all these fake receipts, check out our “Types of fraud” blog to learn more about their tactics.
Threat intel: Template data about fake receipts
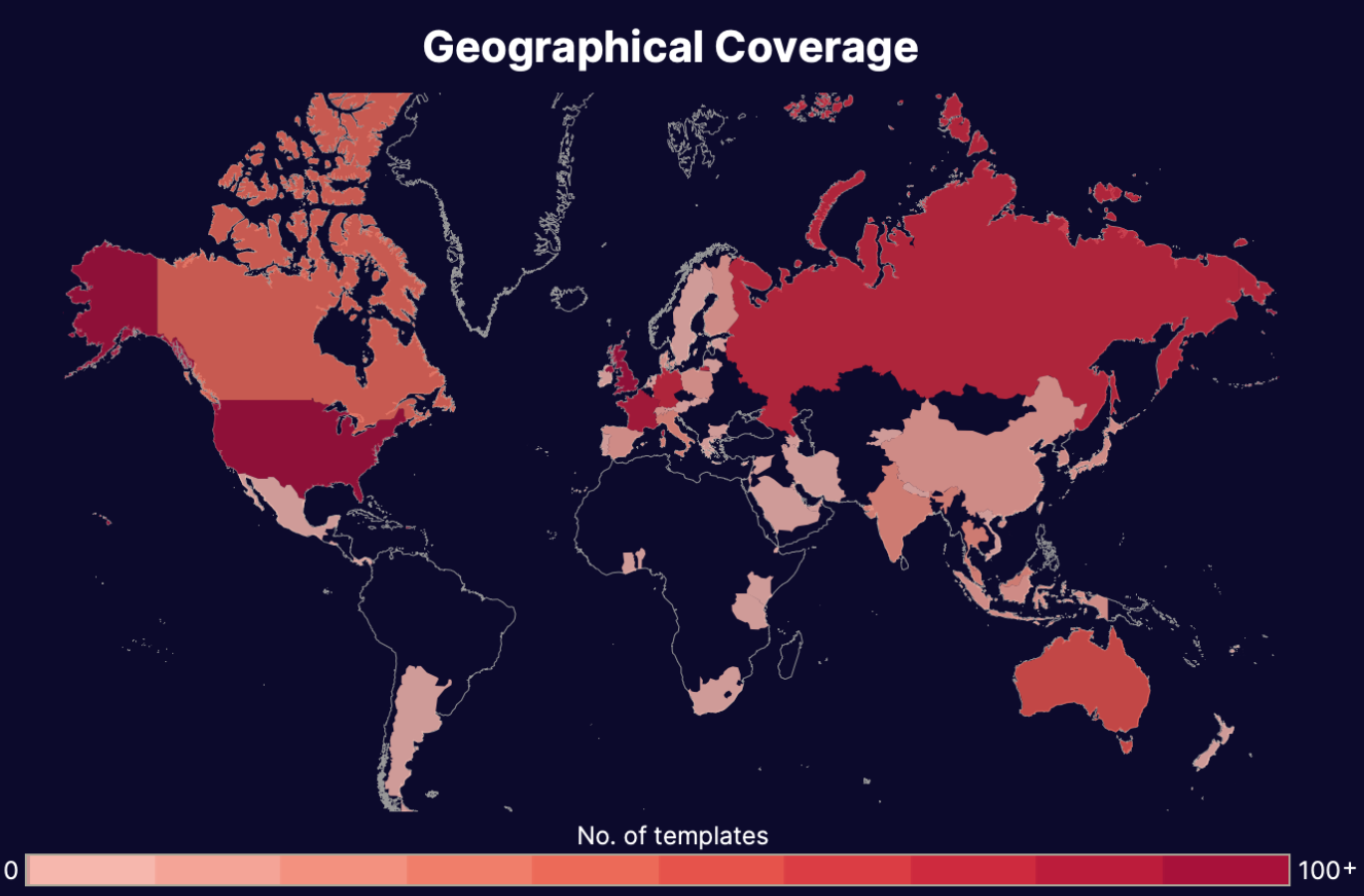
Our Threat Intelligence Unit collects data about template farms which make and distribute fake document templates for fraudulent purposes.
Below, you'll find an infographic containing data about all the fake receipt templates we've found: their availability, their distributors, the institutions or "issuers" whose documents have been exposed, and how much it costs to buy one.
Find more information about the threat these farms pose in our threat intel blog and webinar content.
5 Signs of a forged or fake receipt
If you’re trying to spot fake receipts manually, you need to understand the common warning signs that suggest tampering or receipt fraud. Below are the five core fraud categories, tailored to receipts, with real-world cues you can use to investigate authenticity.
1. Inconsistent formatting
Even across industries, real receipts follow a predictable structure. When that structure is off, it’s often a sign of tampering.
-
Mixed font styles. A sudden switch from Arial to Calibri in the receipts list items.
-
Misaligned totals. If subtotals, taxes, or totals don’t line up with other fields.
-
Poor image scaling. Scanned logos or pixelated barcodes can signal a reassembled receipt.
-
Unusual whitespace or crowding. Broken layouts, crammed fields, or large blank areas usually result from bad or unofficial receipt template use.
-
Missing standard sections. Authentic receipts usually include merchant details, itemization, totals, and payment method.
2. Incorrect or misleading information
Fraudulent receipts often mix accurate and inaccurate data. That blend helps them pass surface checks but falls apart under scrutiny.
-
Wrong tax ID or registration numbers. Compare the business details against official registries or known merchant records.
-
Impossible store hours or timestamps. A purchase timestamp outside business hours.
-
Mismatched store location and purchase. If a receipt from Singapore references a product only available in Ireland.
-
Generic merchant names. Names like “POS Receipt” or “Store #12345” without matching business IDs.
-
Nonexistent product SKUs. Item numbers that don’t return results on brand websites.
3. Bad math and uncharacteristic figures
The arithmetic on a receipt can expose a fake, especially when forgers don't understand the retailer’s tax structure or pricing model.
-
Rounded totals and perfect numbers. Real receipts often include cents and variable totals.
-
Tax inconsistencies. Watch for wrong VAT percentages, or tax applied before discounts instead of after.
-
Item totals that don’t sum correctly. If the subtotal doesn’t match the sum of line items.
-
Duplicate line items with different prices. Two identical items with different unit costs.
-
Mismatch between cash/card and amount paid. If the payment method is “Cash” but the amount ends in .99, double-check. That’s often a digital-only pricing artifact.
4. Receipt-specific inconsistencies
Receipts contain merchant-specific fingerprints, and those inconsistencies are a common giveaway.
-
Outdated branding or logo versions. A 2025 receipt using a 2018 logo (or pre-merger name) is suspect.
-
Third-party payment mentions. Phrases like “PayPal Refund” or “Settled via Square” on a receipt from a company that uses in-house POS systems.
-
Improper receipt language. US-style phrasing like “Sales Tax” on a UK receipt.
-
Missing return policies or footers. Retailers often include store policies or web links.
-
Inconsistent terminal or cashier IDs. Identifiers that change format mid-receipt (e.g., “TID-001” then “1234”).
5. Metadata discrepancies
For digital receipts, the file itself can reveal how it was created — and whether it’s been altered.
-
File creation date post-dates transaction. If a receipt dated February 1, but was generated on April 10.
-
Author field shows editing software. “Microsoft Word” or “Photoshop” listed as the receipt’s creator.
-
Unusual save history. A PDF with no save history or excessive modification timestamps.
-
Inconsistent file naming conventions. Names like “new_receipt_fixed_v2.pdf” that don’t align with professional naming practices.
-
Image-based text. Scanned or screenshot receipts may look real but offer no selectable text.
Disclaimer: Manual inspection alone can't keep pace with modern receipt fraud. High-fidelity forgeries can mimic legitimate formatting and math — right down to barcode logic and tax tiering. That’s why organizations need scalable, AI-powered tools to detect subtle, multi-layered fakes.
How to verify a receipt
There are two ways to spot fake receipts: manual and automated.
While manual reviews are somewhat limited, AI can spot subtle inconsistencies in structure, behavior, and metadata across thousands of documents.
Manual reviews won’t stop fraudsters that now replicate receipts too precisely for visual inspection to reliably catch forgeries.
Still, manual review has its place because many businesses — especially small to mid-size enterprises — haven’t yet upgraded to AI-powered tools.
Eventually everyone will have to modernize.
Manual verification of receipts
Cross-checking your documents against the clear signs of receipt fraud mentioned above is a good place to start. But to go deeper, here are five manual techniques used by compliance teams and auditors when automation isn’t available:
-
Cross-check merchant details. Confirm the business name, tax ID, and address using an official registry like the UK government website or IRS EIN Lookup.
-
Publicly available examples. Such as receipts shared by customers or official samples can be compared to your documents to help verify authenticity.
-
Request proof of payment. Ask for the original payment method confirmation — a matching bank transaction or card charge.
-
Validate tax rates. Look up regional sales tax rates or VAT brackets. Match them against what’s shown on the receipt.
-
Compare to other submissions. Look at the submitter’s prior receipts. Repeated formatting quirks or merchant inconsistencies can expose a pattern.
Keep in mind: Even with attention to detail, manual checks struggle to scale. Forgeries that bypass visual flags (but subtly alter merchant data or payment flow) can slip through undetected. AI-powered systems help close that gap with consistency, speed, and forensic depth.
Using AI and machine learning to spot fake receipts
AI brings consistency, speed, and depth to document verification — all essential in the fight against fake receipts. Where humans see familiar formatting, AI sees mathematical relationships, layout signatures, and behavioral anomalies that forgers can’t easily replicate.
With the right training data, machine learning models can flag minor discrepancies that point to larger fraud patterns. Whether a receipt was altered in a PDF editor, fabricated from scratch, or cloned with AI tools, advanced document forensics can reveal the truth.
Benefits of AI in spotting receipt scams:
-
Template verification. Matches submitted receipts to known layouts used by major retailers and service providers.
-
Field-by-field validation. Compares tax rates, date formats, and price logic against regional or merchant-specific norms.
-
Cross-document matching. Detects when multiple receipts use identical timestamps, merchant IDs, or item codes — a red flag for synthetic submissions.
-
Metadata analysis. Reads embedded file properties to expose creation tools, file modification history, and date conflicts.
-
Continuous learning. AI systems get better with every document they process, adapting to new scams faster than rule-based tools.
Automation vs. AI
Not all automation is created equal. Basic automation follows rules: check that a field exists, confirm the math adds up, flag if a timestamp is missing. These rule-based systems are fast and helpful — until they face a well-crafted fake. If a receipt looks structurally correct but contains fabricated content, most legacy automation won’t catch it.
That’s why automation needs an upgrade.
Modern AI takes everything automation promised and makes it smarter. Many fraud detection systems still rely on inflexible rule sets and miss more subtle structural anomalies. AI upgrades these systems by spotting layout inconsistencies, unexpected field placements, or document structures that deviate from authentic templates, even if the contents appear valid.
We don’t draw this distinction to separate AI from automation — we highlight it because so many verification systems are stuck with rigid logic. Machine learning upgrades those systems with context, cross-field reasoning, and anomaly detection that evolves as fraud tactics do.
When you need to verify receipts at scale only AI-enhanced systems can keep up.
Conclusion
Fake receipts are a persistent threat to financial integrity. Padded expense claims, falsified purchase histories, and the forgery tools to make them are only growing more sophisticated. Even experienced reviewers struggle to distinguish real from fake using manual methods alone.
AI-powered document fraud detection changes that. With the ability to detect subtle inconsistencies in formatting, behavior, and metadata, machine learning enables faster, more accurate detection across entire document ecosystems.
Resistant AI equips organizations with intelligent receipt verification, leveraging cross-document intelligence, forged metadata identification, suspicious relationships between submissions, and hundreds of other detectors. Scroll down to book a demo.
Frequently asked question (FAQ)
Hungry for more fake receipt content? Here are some of the most frequently asked fake receipt questions from around the web.
How to spot fake receipts with AI?
AI detects fake receipts by analyzing patterns, metadata, and anomalies. Machine learning models can identify inconsistencies in layout, font, and data, flagging suspicious receipts for further review.
What’s the difference between receipts, invoices, and bills?
Receipts, invoices, and bills each serve a different purpose in the transaction lifecycle. While typically issued by similar entities, the key distinctions lie in when they’re issued, why they’re issued, and what they confirm.
Receipt: A document confirming that a transaction has been completed and funds received.
-
Characteristics:
-
Issued after payment for a service.
-
Serves as final proof of purchase.
-
Marks the close of a transaction.
-
Affirms that no further payment is due.
-
Typically used for personal records, returns, reimbursements, or audits.
Invoice. A document requesting payment for goods delivered or services rendered.
-
Characteristics:
-
Functions as a formal payment request.
-
Initiates a financial obligation.
-
Usually tied to payment terms or deadlines.
-
Common in business-to-business transactions.
Bill: A notification of charges due, often requiring immediate payment.
-
Characteristics:
-
Issued after service, before payment.
-
Often paid on-the-spot.
-
Often less detailed and formal than invoices.
-
Typically used in hospitality, utilities, or telecom.
Is there software to detect fake receipts?
Yes, software like Resistant AI utilizes machine learning to detect fraudulent receipts by analyzing document features and metadata. These tools can identify subtle inconsistencies and patterns indicative of forgery.
Who needs to check for fake receipts?
Various industries and professionals should be vigilant against receipt fraud:
-
Auditors. To ensure compliance and detect irregularities in financial records.
-
Tax authorities. To verify the authenticity of receipts submitted for tax deductions.
-
Retailers. To detect and prevent return fraud based on fake receipts.
-
Expense approvers. To validate supporting documents before approving employee reimbursements or corporate card transactions.
-
Insurance claims adjusters. To confirm that submitted receipts match claimed losses or medical expenses during the evaluation of a claim.
Is making a fake receipt illegal?
Yes, creating or using fake receipts is illegal and considered fraud. Penalties can include fines and imprisonment, depending on the jurisdiction and severity of the offense. For instance, in Georgia, forging a receipt can lead to felony charges with significant legal consequences.
What are common receipt fraud scams businesses should watch for?
Receipt fraud encompasses various deceptive practices that can significantly impact businesses. Here are some prevalent schemes:
-
Duplicate submissions: Employees submit the same receipt multiple times for reimbursement, exploiting gaps in expense tracking systems.
-
Altered receipts: Legitimate receipts are modified to inflate amounts or change purchase details, often using image editing software.
-
Fabricated receipts: Completely fake receipts are created using online generators or templates to claim nonexistent expenses.
-
Mischaracterized expenses: Personal expenses are disguised as business-related, with receipts manipulated to support the false claim.
How can businesses detect AI-generated fake receipts?
AI-generated fake receipts are increasingly sophisticated, making detection challenging. However, businesses can look for specific indicators:
-
Use the red flags. Look at the red flags we listed in the “Signs of a forged or fake receipt” section and compare them against your submissions. If any of the red flags pop up, escalate for further review.
-
Use an AI-powered fraud detector. Software like Resistant AI’s can help spot AI-generated receipts by detecting unnatural regularities, flagging suspicious structures, analyzing generation artifacts, and learning from fraud trends in the current climate. It doesn’t rely on metadata or easily fooled physical obscurities — instead it provides contextual and structural direct analysis of documents to spot Gen AI fraud.