You might be interested in






Fake W-2 forms have been on the rise since the pandemic in 2020. Governments worldwide began distributing financial aid and unemployment benefits to help citizens manage during the crisis.
However, in the U.S., this approach proved costly. Approximately 10% of pandemic unemployment benefits—an estimated $87.2 billion—were improperly issued.
Organized crime rings and thieves primarily used fake W-2 forms to apply for financial aid during the pandemic.
Now, in 2025, this isn’t just a warning for the US government.
It’s a wake-up call for lenders, employers, and real estate agencies, as fake W-2 form scams can be easily committed by fraudsters using online editing tools and template farms.
This makes detecting document fraud in W-2 forms particularly challenging.
Read on the learn what W-2 forms are, why they're important, how they're being forged, how to identify a fake W-2, and how AI-powered verification solutions can help spot them automatically.
Check out our "How to spot fake documents" blog to learn about more common document forgeries.
A W-2 form, also known as a Wage and Tax Statement, is a document provided by an employer that outlines an employee’s income, taxes withheld from their paycheck, and any benefits received during the fiscal year.
It typically includes:
Employer Identification Number (EIN)
Employer's State ID number
Employee’s income from the last year
Taxes withheld including: federal income tax, Social Security tax, deductions, etc.
Bonuses, tips, and other forms of salary compensation
These details are important for validating the employment history of job candidates or verifying the income of loan applicants and potential tenants.

An example of a W-2 form for illustrative purposes only
Employers use W-2 forms to report Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) taxes and classify employees into full-time workers or 1099s contractors. On the other hand, employees use them to report their income, file federal taxes, and provide proof of income in verification processes.
Here’s a closer look on how W-2 forms serve as a proof of income:
Loan underwriting. Lenders use W-2 forms to verify an applicant’s creditworthiness during the underwriting process. This helps them manage credit risk and minimize their exposure to potential defaults.
Tenant screening. W-2 forms provide information for real estate managers and homeowners to select reliable tenants with steady jobs and consistent income, reducing the risk of unpaid rent and tenant delinquency.
Employment screening. Companies use W-2 forms to verify an applicant’s employment history or to gain deeper insight into a candidate’s financial responsibility and stability, especially for management positions that have access to a company’s financial resources or budgets.
W-2 forms are widely trusted because they’re standardized, IRS-regulated, and directly issued by employers—making them one of the most reliable documents for verifying income and employment history.
Fraudsters tend to commit W-2 fraud using these techniques:
Modifying Genuine W-2 Forms: Perpetrators alter real W-2 forms to fit their needs. For income verification, they may inflate wages and tips to reflect a higher salary and corresponding Social Security taxes or tips. Those attempting to bypass employment verification often change the Employer Identification Number (EIN), employer name, address, and employment tenure.
Creating Custom W-2 Forms: Fraudsters can generate entirely fake W-2 forms using online tools. They fill in false information about employers, income, and other details like the EIN, wages, and employer name.
Using Stolen W-2 Data: Organized crime rings buy genuine W-2 data from online cybercriminal marketplaces. They use this real data to bypass business or mortgage loan underwriting processes to obtain funds illicitly.
If you’d like to know how fraudsters are creating all these fake W-2's, check out our “Types of fraud” blog to learn more about their tactics.
Our Threat Intelligence Unit collects data about template farms which make and distribute fake document templates for fraudulent purposes.
Below, you'll find an infographic containing data about fake W-2 form templates, their availability, their distributors, and how much it costs to buy one.

W-2 forms are in our "tax forms" dataset: documents that contain information for government agencies for the purpose of taxes: W-2 forms, 1099-NEC, P60, P45, etc...
To detect a fake W-2 form scam, it requires attention to detail. The common red flags include:
All W-2 forms should be cross-referenced with other supporting documentation, and due diligence must be conducted. Here are some discrepancies that may indicate fake W-2 forms:
Grammatical or Spelling Errors: Mistakes in specific fields may indicate W-2 fraud: employer’s name, address, or ZIP code.
Debt Section: W-2 forms only report taxes withheld. If debt is present in the document, there is a high chance that it is a fake W-2.
Incorrect EIN Format: Employer Identification Numbers (EINs) should follow the standard 9-digit XX-XXXXXXX format. Any deviations warrant further investigation.
Invalid SSN: Fake W-2 forms may contain invalid Social Security numbers. A major red flag is if the SSN doesn’t follow the correct AAA-GG-SSSS format.
Mismatched Data: Inconsistent personal details, such as the legal name, address, or employer name, when cross-referenced with other documents like bank statements, pay stubs, or identification. Discrepancies between the income deposit date on bank statements and the employment tenure on the W-2 form can also suggest fraud.
A telltale sign of fake W-2 forms is poor formatting. Genuine W-2 forms follow a standardized format, while forgeries often display issues such as:
Font Variations: Different fonts or sizes within the same document.
Alignment Issues: Misaligned text, uneven spacing, or inconsistent margins and columns.
Pixelated Fonts: Blurry or distorted fonts due to alterations.
W-2 forms not in PDF format: W-2 forms that are not in PDF format need to be inspected carefully because they are usually not an original document. Bad actors have the tendency to photograph, scan, or take screenshots of forged or fake documents to hide modifications.
A W-2 form should have a clear breakdown of taxes, deductions, etc, that correspond with the wages. Pay close attention to these warning signs:
W-2 vs Pay stub: If a W-2 form shows a higher wage than a pay stub, it indicates fraud. W-2s report taxable wages after pre-tax deductions, while pay stubs reflect gross earnings.
Round numbers: Rounded numbers can indicate fake W-2 forms because they portray unrealistic precision which deviates from the variances found after deductions, tax withholdings, and benefits.
Incorrect taxes: Taxes that do not align with the salary, such as identical tax amounts for different salaries across several documents, can indicate fraud.
Excessive wages: Salaries that are highly disproportionate to the industry’s average of similarly experienced workers can indicate fake W-2 forms.
W-2 forms come in three copies:
Copy A: This red W-2 form is for informational purposes only and should not be used for verification processes or filed for taxes.
Copy B: This black W-2 form is filed for tax purposes to meet the requirements of the state, city, or local tax department.
Copy C: This copy is for the employee and is used to verify income or employment when requested. Employees are recommended to keep each W-2 form for at least 3 years after they are filed.
Any W-2 form provided other than Copy C is likely a fake.
Here’s a W-2 form in Copy C that should be used for income and employment verification purposes:

Verifying W-2 forms to confirm an individual’s employment and income, (especially in processes like loan approvals, tenant screening, and fraud prevention) can be done either manually or via AI.
While manual checks (such as reviewing formatting, totals, and employer details) can catch obvious red flags, they often miss subtle manipulations or forged entries that bad actors can easily generate with editing software.
That’s why we recommend using an AI-powered document verification solution for verifying W-2 forms to detect tampering, cross-reference data points, and flag anomalies at scale.
Automated verification offers speed, consistency, and resistance to sophisticated fraud tactics—far beyond what manual review alone can provide.
To prevent fake W-2 forms from infiltrating verification processes, start by cross-referencing data with relevant documents and federal sites.
Verify EIN. Checking EIN prefixes and EIN numbers online to verify the listed employers on the W-2 form. If details provided are unclear, contact the IRS Business & Specialty Tax Line at 1-800-829-4933.
Verify SSN online. Verify an applicant’s social security number by checking it online. Here are 3 additional tools:
For income verification, use the Consent Based Social Security Number Verification (CBSV) Service to analyze a large number of SSNs with instantaneous results for a fee.
For employment screening, use the Social Security Number Verification Service to verify the names and SSNs of said employees.
Free services such as SSN-Check allows a quick check of issued SSNs but this tool does not validate the SSNs of employees and non-employees.
Check tax withholding rates. Cross-reference listed taxes with IRS data to ensure accuracy.
Check with employers. Call the employers listed on the W-2 to verify the applicant’s income, address, and legal name to confirm the authenticity, rule out W-2 form fraud, and verify the applicant’s employment history.
Cross-reference all documents. Ensure consistency in all details such as legal name, address, wages, and other information across tax returns, pay stubs, bank statements, and other documents.
Keep in mind: Using these resources to verify income is not sustainable in the long run—especially for companies that need to process large volumes of W-2 forms.
With the prevalence of large-scale template farms and online editing tools, creating fake W-2 documents has become easier, making it tough for underwriters, employers and property managers to detect fake W-2 forms.
This makes manual inspections less effective and far more time-consuming as the naked eye struggles to spot subtle changes in metadata, formatting, and fonts.
Automated or AI-driven document fraud detection services can help underwriters and tenant screeners assess the authenticity of W2s with more speed and accuracy, giving them greater confidence in their decision-making, and allowing them to process a much greater volume of documents.
Combined with an intelligent document processing system, AI has the potential to radically transform your processes in a safe way.
Deploy a fake W-2 form detector app: Before processing a document, you should understand if you can trust it, so fraud detection is the first step. One way is to deploy a dedicated AI document fraud detector to spot fake or forged W-2 forms.
Use an Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) solution: Since W-2 forms follow a structured format, IDP solutions can efficiently extract, process, and cross-reference information with external sources like credit bureaus or financial institutions. The key is to automate document processing with fraud detection solutions that help mitigate risks and prevent fake W-2 forms from slipping through the cracks.
Together, these technologies not only reduce risk and manual workload, but also establish a foundation of trust and scalability in your verification workflows.
Resistant AI’s document forensics software acts as a "bionic eye" for underwriters, employers, and tenant screeners. Designed to detect fake or forged W-2 forms in under 20 seconds, it identifies subtle indicators of fraud that often go unnoticed by the human eye.
With Resistant AI, verifying any document, whether a PDF or image, takes less than 20 seconds, and can speed up review processes fivefold while still catching 3x more fraud to mitigate risks and protect themselves from fraud.
Scroll down and book a demo to eliminate fake W-2 forms from your process today.
Hungry for more fake w-2 form content? Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about checking for fake W-2s from around the web.
AI and machine learning greatly enhance a company’s income verification processes by improving precision and accuracy in detecting fraudulent W-2 forms—with low false positives. Here are five essential components that a good AI document fraud detection software should have:
High accuracy. An AI-powered document fraud detector must verify W-2 forms with a high level of accuracy to give underwriters, employers, and tenant screeners the confidence to process large volumes swiftly. This includes identifying subtle signs of forgery, fake templates, and other fraud indicators that are often undetectable to the human eye, ensuring that fraudulent W-2 forms don’t slip through income verification processes.
Support for multiple document formats. An AI document fraud detection software that analyzes different document formats like PDF, JPEG, and PNG facilitates smoother proof of income processes by giving customers more options to submit documents.
Clear verdicts. A high-quality AI document fraud detector should provide clear verdicts that do not need further interpretation—enabling you to approve or deny W-2 forms based on clear, evidence-backed results to minimize potential risks.
Explainable results. Explainable results enable underwriters, employers, and tenant screeners to understand the risk each W-2 form carries, helping them assess its authenticity and verify an applicant’s income.
Configurable to match your risk appetite. The best AI document fraud detector can be configured by businesses to detect outcomes with their risk appetite—only approving W-2 forms that only come in certain formats, for example.
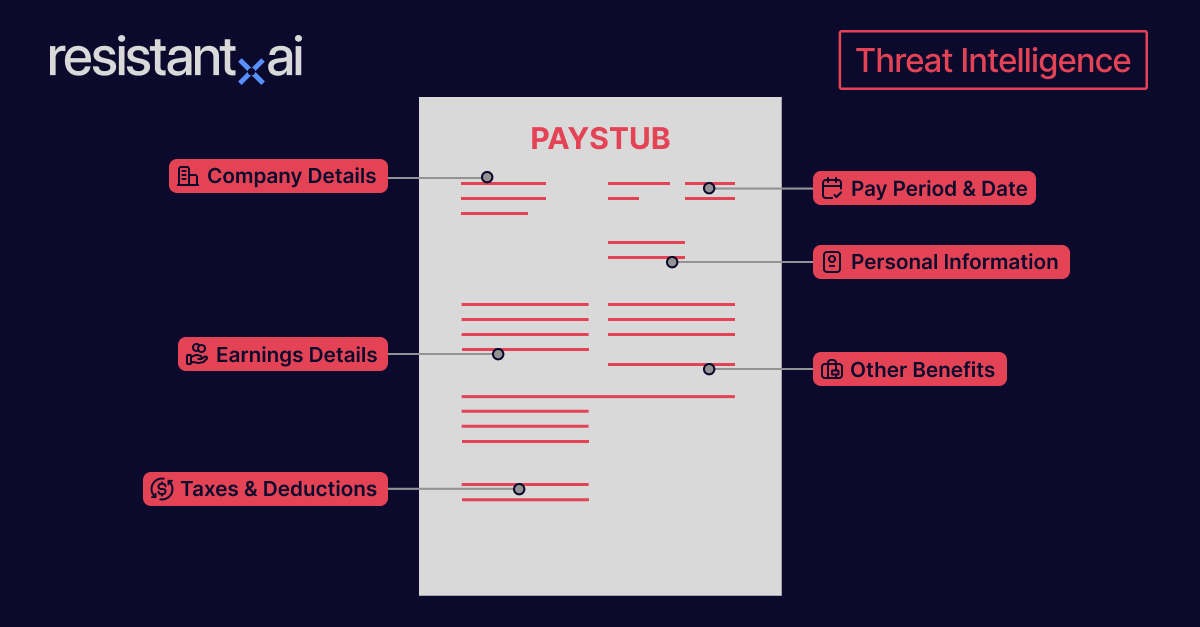
A pay stub is a document that records an employee’s earnings and deductions, while a W-2 form, also known as a wage and tax statement, is a US document provided by employers for tax reporting.
Yes, Resistant AI offers advanced software that detects fake W-2 forms using machine learning and forensic analysis. It analyzes formatting, metadata, numerical inconsistencies, and cross-references employer and payroll data to identify signs of tampering or forgery with greater accuracy than manual reviews.
Yes, creating or using a fake W-2 form is illegal and considered a form of fraud. It can lead to criminal charges, fines, and even prison time, especially when used to deceive financial institutions, government agencies, or employers.
Several roles rely on W-2 forms as a trusted source of truth for income and employment verification — making document integrity essential. Here are some of the most common:
Loan officers and underwriters. To verify a borrower’s income and employment during the loan approval process, ensuring the applicant has the financial means to repay.
Landlords and property managers. To assess an applicant’s income stability before signing a lease, reducing the risk of unpaid rent.
HR and employment verifiers. To confirm prior income and job history during background checks or when onboarding employees with sensitive roles.
Government agencies. To validate income claims for benefits eligibility, tax credit assessments, or compliance with public assistance regulations.
Fraud and risk teams. In fintech and identity verification platforms, to spot synthetic identities or manipulated documents used in account creation or financial scams.
The latest version of a W-2 form can be found on the official IRS website.
There is no standardized method for employers to verify W-2 forms. Depending on their workflow, some may incorporate document fraud detection systems, while others rely on manual reviews and cross-referencing with external agencies.