You might be interested in






As businesses expand faster than ever across digital and physical markets, the demand for legitimate proof of authorization (like a business license) is critical. Especially in 2026. As recently as summer 2025, a fake business license syndicate was busted up in Kenya.
Unfortunately, fraudsters have taken advantage of generative AI tools and document editing software to create fake business licenses that look strikingly authentic.
Access to free fraud templates online has made it easier than ever to forge convincing documents, putting banks, marketplaces, and regulatory institutions at significant risk.
Business licenses are essential for validating an entity is authorized to operate legally within a jurisdiction, ensuring regulatory compliance, and preventing financial crimes. Spotting document fraud within them is imperative.
Read on to learn what a business license entails, how fake licenses are made, how to spot one, and how AI-powered document verification solutions can automate and protect your processes.
Check out our "How to spot fake documents" blog to learn about more common document forgeries.
A business license is an official document issued by a government authority, granting permission for an entity to legally conduct business activities within a specific jurisdiction.
A business license typically includes the following components:
Business name and official license number.
Issuance date and expiration date.
Type of business activities permitted.
Issuing city, county, or state authority.
Business owner's name and address.
Physical business location.
Fees paid or proof of payment details.
This information plays a crucial role during vendor onboarding, KYB (Know Your Business) processes, licensing renewals, and financial auditing.

An example of a business license for illustrative purposes only
A business license serves as official proof that an organization operates legally and adheres to local laws and tax codes. It is foundational for document verification in the following industries:
Banking and financial institutions: Verifying legitimacy before opening accounts or extending credit lines.
Real estate transactions: Confirming operational legality for property leasing or purchases.
Procurement and vendor management: Ensuring suppliers are properly licensed for their goods or services.
Regulatory compliance checks: During AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYB processes.
Government contracts and grants: Eligibility for bidding on projects or receiving public funds.
It remains one of the most trusted documents during risk assessments because it carries direct legal authority from government bodies. Since nearly every legitimate business is required to hold a license, it's typically easy for businesses to provide one when asked.
As part of the UK’s drive to make corporate information more reliable and harder for fraudsters to abuse, the Economic Crime and Corporate Transparency Act 2023 is reforming Companies House and rolling out enhanced identity verification and transparency measures through 2026.
The legislation gives registry authorities stronger powers to challenge, remove or refuse inaccurate or false corporate filings and aims to make the company register more trustworthy. This shift could lead to fraudsters targeting supporting documents that directly impacts how financial institutions should think about validating business licenses.
If you’d like to know how fraudsters are creating all these fake business licenses, check out our “Types of fraud” blog to learn more about their tactics.
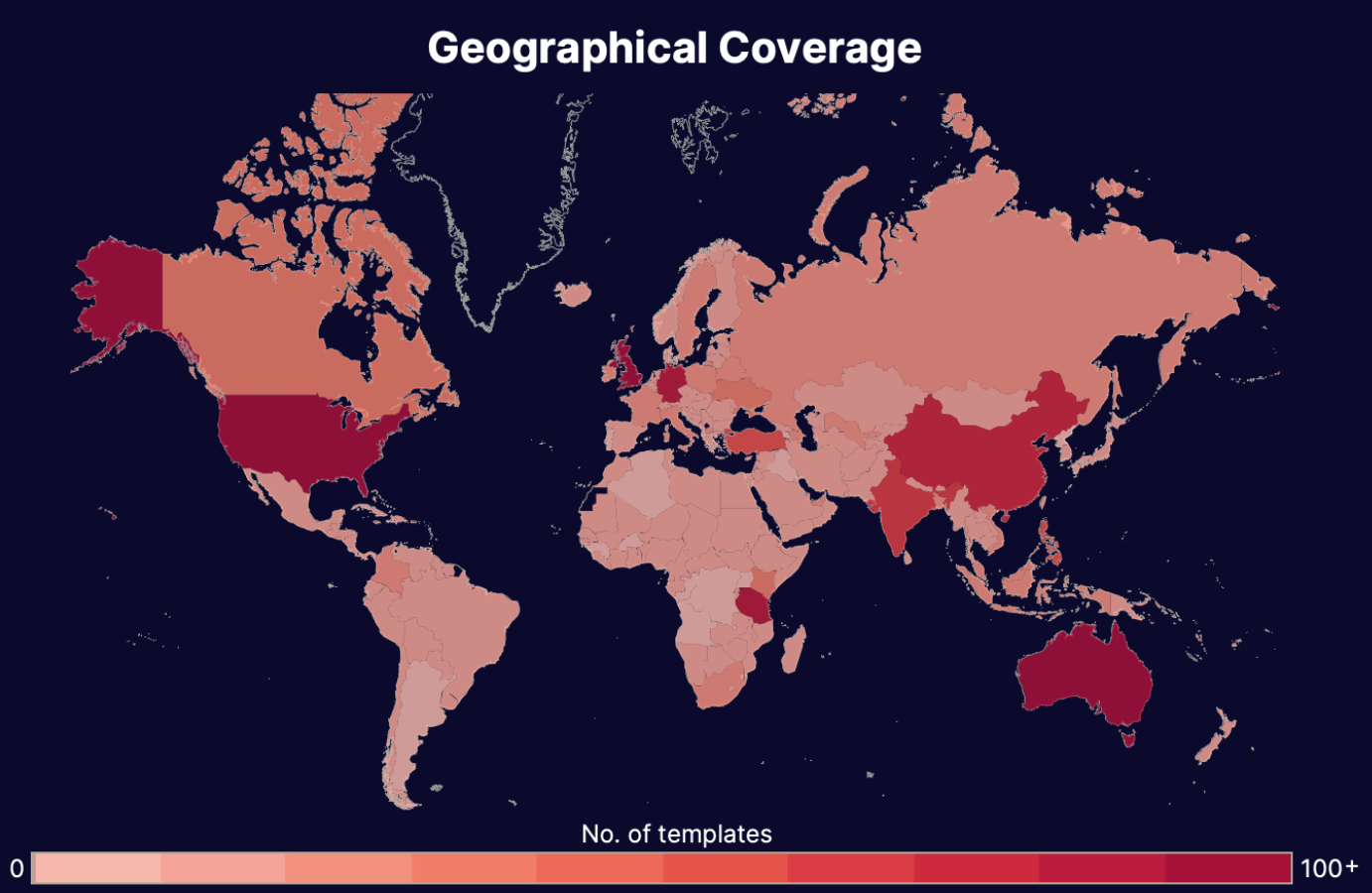
Our Threat Intelligence Unit collects data about template farms which make and distribute fake document templates for fraudulent purposes.
Below, you'll find an infographic containing data about fake business license templates, their availability, their distributors, the institutions or "issuers" whose documents have been exposed, and how much it costs to buy one.
Business licenses are in our "company information" dataset: documents that contain information about a company like certificates of incorporation, articles of organization, professional licenses, trade licenses, etc.
If you want to detect business license fraud manually, focus on common red flags that often indicate forgery. Here are the most common with specific business license examples:
Authentic business licenses come from standardized templates with strict formatting guidelines. Signs of inconsistency include:
Font mismatches. Different typefaces or font sizes across sections (business name vs license number).
Poor alignment. Texts like the license number or city seal not centered or misaligned.
Absent headers or footers. Missing standard elements like official city seals, borders, or standard license frames.
Low-quality images. Pixelated emblems, distorted barcodes, or blurry watermarks.
Incorrect capitalizations. Unprofessional variations in capitalization of business names or government agencies.
Suspicious file formats. Licenses provided in JPEGs, screenshots, or editable Word docs instead of secured PDFs.
Fake licenses often contain data errors that don’t align with official records:
Unregistered business name. Cannot be found in public or state databases.
Jurisdiction mismatch. A business operating in Florida holding a license from California agencies.
Date anomalies. Licenses showing unusually long validity periods (e.g., 10 years instead of annual renewal).
Fake license numbers. Random or incorrectly formatted licensing numbers.
Incorrect addresses. Listing residential addresses for commercial licenses.
Activity mismatch. A "retail" business license listed for a construction company.
Check for numeric inconsistencies that are not typical of real licenses:
Unrealistic license fees. A liquor license listed as costing $10 when standard fees are $300+.
Invalid activity codes. Nonexistent or made-up business classification codes.
Unusual license types. Terms like “universal operation license” that don’t exist in regulatory frameworks.
Duplicate expiration dates. Different sections of the license showing different expiry dates.
Internal contradictions often reveal forgeries:
Conflicting business types. Labeled both as a "Home Occupation" and "Retail" establishment.
Multiple owner names. Different individuals listed as responsible parties in various sections.
Incorrect terminology. Using casual language instead of legal terms like "Permittee" or "Licensee."
Signature anomalies. Copied-and-pasted signatures or electronic stamps with mismatched agencies.
Always check the document's metadata for hidden tampering:
Unauthorized software usage. Created or edited with Photoshop, Canva, or Microsoft Word.
Missing e-signatures. No government certification, seals, or timestamps.
Timing inconsistencies. Creation date doesn't align with the issuance date on the license.
Wrong authorship. Author metadata shows an individual, not a government licensing body.
Disclaimer: Manually checking every field is slow, laborious, and prone to human error. Fraudsters are improving fast—which is why AI document verification is now essential.
There are two ways to verify a business license: manual validation and AI-powered automation.
While manual business license fraud verification is certainly an option, AI is far more effective.
AI-powered tools instantly cross-check licenses against official databases, detect hidden forgeries, and flag inconsistencies in formatting, metadata, and document structure.
At scale, AI offers faster, more reliable, and more fraud-resistant verification—making it the preferred method for modern businesses.
Procurement managers, loan underwriters, real estate leasing agents and other roles that need to check business licenses can perform the following (otherwise, it could indicate a business license scam):
Cross-referencing government databases: Search city or county licensing portals.
Validating license numbers: Match numbers to records on Secretary of State websites.
Confirming business ownership: Research using third-party databases like Orbis or OpenCorporates.
Contacting issuing agencies: Directly reach out to the city or county licensing department.
Cross-checking company details: Review LinkedIn profiles, Crunchbase, or ZoomInfo listings.
Requesting notarized license copies: Directly from business owners when in doubt.
Keep in mind: These manual methods are time-consuming and may not keep pace with evolving fraud techniques.
AI-powered business license fraud detection (like ours at Resistant AI) streamlines business license verification at scale:
Instant document verification. Real-time checks against local and global registries.
Anomaly detection. Identifies font mismatches, metadata inconsistencies, and synthetic document patterns.
Seamless integration. Embeds easily into onboarding, CRM, and KYB workflows.
Regulatory audit trails. Automated logs of verification steps for compliance reporting.
AI tools continue learning with every new fraud case, staying ahead of criminals who rely on outdated human checks.
Automation tools rely on predefined rules to verify business licenses, such as checking for expected fields or matching license numbers to known formats.
While this works for standard cases, it breaks down when documents deviate from templates, include unexpected layouts, or come from unfamiliar jurisdictions.
AI, on the other hand, can learn from real-world data, adapt to variation, and detect fraud patterns that rigid automation would miss entirely.
Fake business licenses represent a growing fraud threat in 2025. Organizations that rely solely on manual review risk falling behind—and falling victim.
By using layered, AI-powered document verification, your business can prevent fraud before it causes operational or reputational damage.
Scroll down and click the "Book a Demo" button to see how Resistant AI can protect your organization from document fraud!
Hungry for more fake business license content? Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about fake business licenses from around the web.
AI-powered document verification tools can spot fake business licenses by analyzing layout inconsistencies and metadata discrepancies. Machine learning models detect subtle fraud signals—like reused templates, tampered fonts, or fabricated data—that manual reviewers often miss, allowing businesses to catch even highly sophisticated forgeries instantly.
Business licenses and business registration certificates serve different legal and operational purposes. Registrations prove existence while licenses permit operation.
Business license. A legal authorization issued by a government body allowing a business to operate within a specific jurisdiction.
Issued by: Typically city, county, or state licensing departments.
Unique characteristics:
Activity-specific (e.g., retail, construction).
Often needs annual renewal.
Required for day-to-day operations.
Business registration certificate. A formal record confirming a business's legal creation and existence (often referred to as a Certificate of Formation or Incorporation).
Issued by: Usually Secretary of State offices or corporate registries.
Unique characteristics:
Documents the creation of the entity itself (LLC, Corp).
Usually required only once at founding
Not tied to specific activities or local compliance.
Yes! Platforms like ours at Resistant AI offer advanced document fraud detection software that can automatically verify business licenses, flag suspicious modifications. We allow businesses to automate compliance workflows, reduce manual errors, and protect themselves against sophisticated document fraud schemes.
Absolutely. Producing, altering, or using a fake business license scam is considered fraud and is illegal in virtually every jurisdiction.
Penalties for business license fraud can include hefty fines, criminal charges, civil lawsuits, and even imprisonment—especially if the forgery leads to financial losses, regulatory violations, or public harm.
Several roles across industries are responsible for verifying business licenses, including:
To check if a company is legitimate, you should:
For larger-scale verification or onboarding, using AI document verification tools can make this process faster, more accurate, and more fraud-resistant.


