You might be interested in






The prevalence of fake pay stubs surged in 2025, and 2026 numbers are about to go even higher. Fake pay stub generators and template farms, are making the crime easier to commit than ever before.
200+ pay stub templates are available on sites like Doc Juicer, making the production of fakes surprisingly simple.
Organizations need pay stubs documents for loan and lease approvals. They serve as a proof of income for lenders, property managers, and employers. Spotting document fraud in pay stubs is imperative.
Read on to learn about the threat of fake pay stubs, how they're being faked, how to spot a fake, and how document verification solutions can spot fake documents automatically.
Check out our "How to spot fake documents" blog to learn about more common document forgeries.
Our Threat Intelligence Unit collects data about template farms which make and distribute fake document templates for fraudulent purposes.
Below, you'll find an infographic containing data about all the fake pay stub templates we've found: their availability, the institutions or "issuers" whose documents have been exposed, their distributors, and how much it costs to buy one.
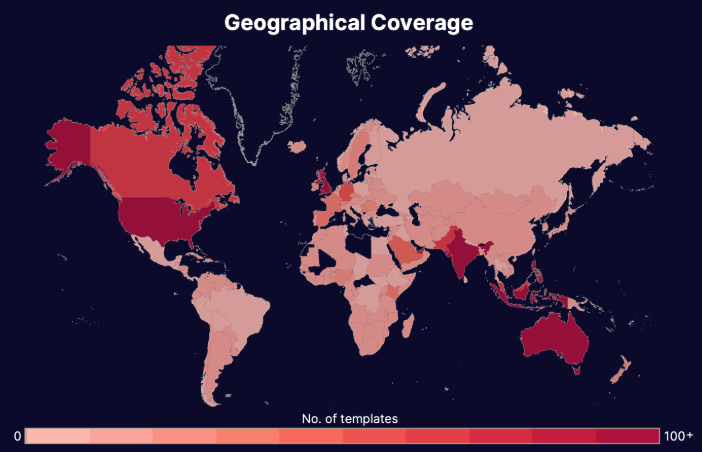
Pay stubs are a part of our "income confirmation" dataset which includes documents like pay stubs, pay slips, earnings statements, etc. Find more information about the threat these farms pose in our threat intel blog and webinar content.
Outside of these publicly available templates, there's also the threat of pay stub generators to consider.
In theory, they do have legitimate use cases for pay stub generators. Freelancers, contractors, seasonal workers, or very small businesses may not have access to formal payroll software. These tools can offer a quick way to formalize income documentation.
But in practice, their use raises questions. Any organization large enough to employ multiple workers consistently will typically invest in dedicated payroll software or outsource payroll processing altogether.
These systems generate pay stubs directly from payroll data and maintain records tied to tax reporting and wage payments.
When a pay stub appears comes from a generic online generator rather than a payroll system, it suggests the document may have been created outside the employer’s actual payroll workflow: a gap that fraudsters are increasingly willing to exploit.
“Pay stubs are highly diverse and often created in unusual (or even suspicious) ways. We've seen everything from legitimate payslips generated using online tools to documents created with MS Excel templates. A single perspective isn't enough. You need a full ensemble of detectors to uncover events across the document's lifecycle: how and where it was created, whether it has been modified, if it resembles known formats, and whether its ”

A pay stub, also called a payslip in the UK, is a document provided by an employer that outlines an employee's earnings and deductions for a specific duration. It also acts as a proof of income document for loan applications, rental agreements, and employment contracts.
A pay stub typically includes:
Employee information. Name, address, and Social Security number.
Employer information. Company name, address, and tax identification number.
Earnings. Gross pay, net pay, and hours worked.
Deductions. Taxes withheld, benefits, and other deductions.
These details help assess an applicant’s financial stability, enabling them to make informed decisions. 
An example of a pay stub for illustrative purposes only
Pay stubs are the most common documents used for proof of income across specific situations, such as:
Loan underwriting. Lenders use applicant pay stubs to verify creditworthiness during the underwriting process. This helps them manage credit risk and minimize their exposure to potential defaults.
Tenant screening. Pay stubs give landlords key information to choose reliable tenants with steady jobs and consistent income, reducing the risk of unpaid rent and tenant delinquency.
Employment screening. Companies verify applicant pay stubs to gain deeper insight into a candidate’s financial responsibility and stability, especially for management positions that have access to a company’s financial resources or budgets.
Mortgage underwriting. Lenders use utility bills as proof of address to verify where a mortgage loan applicant currently lives. This helps prevent potential fraud and missed payments by ensuring applicants aren't applying for loans from a different location.
Pay stubs are the most common document for providing proof of income because they are consistent, detailed, recent, and readily available. They include all of the essential information (i.e., gross pay, net pay, deductions, and employer information) while being offered universally by almost every employer in both physical and digital format.
If you’d like to know how fraudsters are creating all these fake pay stubs, check out our “Types of fraud” blog to learn more about their tactics.
One way to detect fraudulent pay stubs is to pay attention to red flags that indicate suspicious activity. Here’s a comprehensive list to help you spot fake pay stubs effectively:
A telltale sign of fake pay stubs is irregular formatting. Authentic pay stubs usually follow a standardized format, while fake ones may have discrepancies such as:
Font variations. Different fonts and sizes used within the same document.
Alignment issues. Misaligned text, uneven spacing, margins or columns.
Poor presentation. The overall document looks unprofessional, untidy, or crooked.
Missing data. Personal details of the applicant, such as tax identification number, full legal name, or address, may be missing or omitted.
Pixelated logos or fonts. Altered pay stubs tend to have distorted fonts or logos.
Low-quality watermarks. Fake pay stubs usually feature unprofessional-looking watermarks with poor resolution or incorrect sizes.
Faded or blurry texts. Washed-out or smudged texts can indicate fake pay stubs, as most companies use high-resolution typefaces.
Pay stubs not in PDF format. Pay stubs that are not in PDF format should be scrutinized because you are not dealing with the original document, and fraudsters may have taken screenshots or photos in order to hide modifications.
All pay stubs should ideally be cross-referenced with other documentation to verify the information and identity provided by the applicant, ensuring accuracy and authenticity. Common informational red flags for pay stubs include:
Employee details. Misspellings or incorrect Social Security numbers.
Employer information. Employer’s details that do not match official records.
Inconsistent information. Gross pay is lower than the net pay, or the applicant’s legal name varies across different documents.
Mismatched data after cross-referencing. Personal details, such as legal name, address or employer name differ from other documents (like bank statements or identification documents). Discrepancies between income listed on the bank statements and the pay stubs may indicate fraud.
Inconsistent address. Fraud may be suspected when the employee works and lives in different states, with inconsistent addresses across their bank statements, credit reports, pay stubs, etc.
A real pay stub’s sums and totals should always be accurate, including deductions that correspond with the net salary. They should also fall in line with industry averages and standards. Here are some red flags to watch out for:
Pay stub to W-2 mismatch. A major red flag occurs when the final pay stub shows a lower wage than the W-2 form, which is impossible since W-2 forms report all taxable income.
Salary discrepancies. Annual salaries listed on a biweekly or monthly pay stub may indicate pay stub fraud.
Round numbers. Rounded numbers for net wages may indicate fraud. It is highly unlikely to maintain a round number after benefits, deductions, and taxes.
Exorbitant wages. Salaries that are significantly higher than the industry’s average may signal pay stub fraud.
Lack of an hourly rate. American pay stubs should indicate an hourly rate. However, European and some Asian countries use monthly pay stubs—except Japan, which issues bi-monthly pay stubs.
Incorrect taxes. Taxes that don’t align with the salary, such as identical tax amounts for different salaries across several documents, can indicate fraud.
Bonus payments. Bonuses that do not align with the job position or industry averages are suspicious.
Excessive overtime. Part time roles showing unrealistic overtime, such as 80 hours or more in a month, could be fraudulent.
Pay stubs often include official branding from the employer, consistent pay dates, and a professional appearance. Falsified pay stubs usually have inconsistencies such as:
Lack of contact information. Altered pay stubs often lack contact details for HR or payroll departments.
Abnormal pay day. Pay periods typically start at the beginning or end of the week, so a pay stub showing a payday in the middle of the week may be suspicious.
Inconsistent pay periods. Pay dates that vary unpredictably throughout employment may indicate pay stub fraud.
Prompt payment. Falsified pay stubs might show salaries paid the day after the invoice is issued—which is highly unusual.
Missing sections. Fake pay stubs often omit details on benefits, retirement contributions (such as 401K), and taxes—which are usually present on real pay stubs.
Altered pay stubs can contain metadata discrepancies that indicate forgery. Pay attention to the following:
Time stamps. Different time stamps do not always indicate fraud, as creation and modification dates can be altered automatically by software. However, cross-referencing pay stubs with other documents can help spot inconsistencies. If a pay stub’s creation and modification date is before the pay period or has irregular payment processing timelines, it may indicate pay stub fraud.
Production software. The “producer” field shows the software used to produce the document. It should never list software like Photoshop, which are commonly used to modify documents.
Creator. “Creators” indicate which program modified the document. If a PDF editor is listed, it might suggest that some aspects of the pay stub have been modified.
Author. This field shows who modified the document. If it lists the applicant’s name, it raises concerns; if it shows the employer’s name, the pay stubs are likely genuine.
Disclaimer: Manual reviews of metadata have limitations as experienced fraudsters can modify a file’s metadata, making it difficult to detect document fraud through visual inspection alone.
For this reason, using an AI document fraud detection tool significantly enhances the ability of lenders, property firms, and employers to prevent document fraud.
There are two primary ways to verify applicant pay stubs: conducting manual reviews or using AI software.
We recommend a layered AI paystub checker due to the sophisticated defrauding techniques used to create fake pay stubs.
Manual inspections are less reliable as the naked eye often fails to detect minute changes in metadata, formatting, and even fonts.
Still, manual review has its place in the fake pay stub identification process. Cross referencing documents with known channels and reliable sources is a nice start. But you’ll need to move on to an AI solution to successfully combat fake pay stubs at scale.
Underwriters, landlords, and property managers can reduce pay stub fraud by exercising due diligence and cross referencing data across all relevant documents and channels. Here’s how:
Contact employers. Call the applicant’s employers to verify their legal name, address, and income. This helps to confirm the applicant’s identity and ensures that only traceable, real pay stubs are submitted.
Check identification numbers. Verify tax identification (TIN) or Social Security numbers online using governmental sites. For European applicants, check TIN; for American applicants, verify with the IRS or the SSA.
Calculate taxes. Cross-check tax returns or deductibles listed on the pay stubs with the IRS or other tax agencies to ensure accuracy.
Use the IRS. Request applicants to enable the Income Verification Express Service so you can obtain official tax transcripts, which can be cross referenced with submitted pay stubs.
Cross-reference all documents. Ensure consistency in the legal name, address, wages, and other information across all documents and systems including tax returns, pay stubs, bank statements, etc.
LinkedIn. Review the applicant’s LinkedIn profile to confirm that their work history aligns with the pay stubs they’ve submitted.
Keep in mind: These tasks are costly, labor-intensive, and time-consuming for lenders, real estate firms, and employers to spot fake documents.
Manual due diligence can prevent firms, especially fintech lenders, from scaling efficiently when applicants seek a faster loan application process.
This is why AI-powered fraud detection solutions exist.
Using AI and machine learning as a paystub checker for document verification can greatly help lenders, real estate firms, and employers mitigate risks and scale fraud prevention and detection efforts.
The best approach to verifying applicant pay stubs involves combining document fraud software and document processing tools for fast and accurate results. Here are some technologies that can help:
Deploy a fake pay stub scanner. AI-powered document fraud software can detect fake paycheck stubs within seconds while indicating exactly where and when forgery occurred.
Extract content with an Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) solution. IDP is an effective way to process, extract, and cross-check data with external sources like employers, credit bureaus or other financial institutions. Automating document processing workflows without errors ensures a reliable and efficient method for identifying fraudulent pay stubs.
Combining these solutions streamlines the income verification process. By using automated tools, lenders, landlords, and property managers can save valuable time and resources, allowing them to focus on scaling their business.
Fake pay stubs are more convincing, more accessible, and more common than ever—making manual detection methods both risky and inefficient. As fraud tactics grow more sophisticated, the only scalable, accurate way to stay ahead is with AI-powered document verification tools built to catch what humans can’t.
With Resistant AI’s automated document fraud detector, lenders, landlords, and property managers can effectively spot altered or fake pay stubs in under 20 seconds.
Save up to 52 minutes per case investigation and still detect 32% more fraud, effectively preventing potential losses and saving your business time.
The software is user-friendly, featuring a drag-and-drop function that seamlessly integrates the income verification process within a firm’s existing workflows.
Scroll down to book a demo and learn more.
Still hungry for some more fake pay stub content? Here are some frequently asked questions about fake pay stubs we found around the web.
We already mentioned how AI-driven document fraud detection software can benefit businesses right away. Intelligent document processing solutions combine OCR with large language models to analyze the content of a document and search for inconsistencies with other sources and universal anomalies. They are content agnostic and focus on the overall structure of the doc as opposed to what it’s actually saying.
Making a fake pay stub is not illegal but using it as a proof of income is. This can lead to hefty penalties or even jail time.
Document fraud detection software like Resistant AI can help detect falsified pay stubs in under 20 seconds, as well as any other type of modified or fake document.
No, a paycheck indicates the amount earned, while a pay stub provides a detailed breakdown of earnings.
A pay stub is a document that records an employee’s earnings and deductions, while a W-2 form, also known as a wage and tax statement, is a US document provided by employers for tax reporting.
Both documents can serve as proof of income, but they have distinct differences:
A pay stub shows the earnings for a specific pay period, while a W-2 form reports an employee’s annual income.
Pay stubs focus on gross wages whereas W-2 forms display taxable income for the entire fiscal year.
Non-taxable benefits (such as health savings accounts, fringe benefits, bonuses, additional overtime, or other deductions) are present on pay stubs, but not on W-2 forms.
Employers must send W-2 forms to all employees by the end of January for the previous fiscal year, but pay stubs are usually issued monthly or biweekly.
Bonuses, overtime pay, and extra income are categorized differently on W-2 forms compared to pay stubs.
Despite these differences, both types of proof of income documents can be falsified or modified to pass certain criteria in the tenant or loan application process.
Fake pay stubs are commonly used to inflate income, falsify employment, or fabricate job history. The following teams and industries rely on pay stub verification and are frequent targets of document fraud:
Loan underwriters. Check pay stubs for accurate income verification during credit applications, especially for auto loans, personal loans, and mortgages.
Landlords and tenant screening services. Use pay stubs to confirm that an applicant earns enough to cover monthly rent and living expenses.
Buy-now-pay-later providers. Rely on pay stubs to assess short-term repayment ability for users without an established credit file.
Credit card issuers. Sometimes request pay stubs to confirm reported income for new credit lines or limit increases.
Government agencies. Use pay stubs to determine eligibility for benefits, subsidies, or income-based housing programs.
Gig economy platforms. May request pay stubs to validate employment status for platform access, insurance coverage, or earnings-based tiers.
Employers and HR teams. Occasionally review pay stubs when onboarding contractors or verifying income history during background checks.
Fraud investigation units. Scrutinize pay stubs during internal or external investigations tied to claims, loans, or identity fraud.


