How to spot fake EIN verification letters


In 2025, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) warned businesses about websites charging up to $300 for Employer Identification Numbers (EINs) while falsely claiming affiliation with the IRS. Unfortunately, this was only foreshadowing what has become an even larger problem in 2026.
That same demand for official EIN documentation has fueled a surge in fake EIN verification letters, often created using online document templates or AI-driven forgeries.
These letters, also known as IRS CP 575 notices or 147C letters, are a crucial part of business verification processes. They’re frequently requested by banks, lenders, payment processors, and government agencies to confirm that a company truly exists and is properly registered with the Internal Revenue Service.
Fake EIN letters are used in business identity theft, loan scams, and fraudulent vendor onboarding.
A forged letter can give a fraudster access to financial services or government programs under a false identity — putting organizations at serious risk of compliance violations, fines, and financial losses.
Read on to learn what an EIN verification letter is, how fraudsters are faking them, what red flags to look out for, and how AI-powered tools can help your business detect fake EIN verification letters before they cause damage.
Check out our “How to spot fake documents” blog to learn about more common document forgeries.
What is an EIN verification letter?
An Employer Identification Number (EIN) is a 9-digit official registration number issued by the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS). It serves as proof that a business has been officially registered with the IRS, uniquely identifying it for tax reporting and compliance purposes for companies, nonprofits, and other entities.
U.S. companies need them and also foreign companies that interact with the U.S. tax system.
An EIN verification letter is an official document that serves as proof of a business’ EIN number. There are two main types of EIN verification letters:
- CP 575 notice. The original confirmation letter the IRS mails when a business first applies for and receives its EIN through Form SS-4. It contains the EIN, the business’s legal name, and instructions about tax filing responsibilities. Importantly, the IRS only issues this letter once, right after the EIN is created. If the business misplaces it, the IRS will not send another CP 575.
- 147C letter. The official replacement document businesses can request if the CP 575 is lost or never received. A 147C letter provides the same essential information (the business’s name, EIN, and IRS contact details) and is accepted by banks, lenders, and regulators as proof of EIN validity.
Both documents are accepted as official IRS proof of a business’s EIN, but the 147C letter is the one most commonly seen in modern verification workflows since organizations often need replacements years after formation.
Key elements of an EIN verification letter include:
- IRS letterhead and seals. Official branding, formatting, and government insignia that validate the document’s source.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN). A nine-digit number in the format XX-XXXXXXX.
- Business name and mailing address. Must match the information on IRS records.
- Responsible party details. The name of the individual legally responsible for the business.
- Date. Date of the letter’s issuing.
- Form type. The request form you filled out to get the letter (usually SS-4).
- Number of the notice. Often labeled as “CP 575” (original notice) or “147C” (verification copy).
- State, city, office number. The state, city, and identification number of the IRS office that sent the letter.
- Letter body. Typically the same wording, thanking the company for applying and outlining the parameters of the letter and this document.
- Important reminders. Rules and best practices for the use of the letter.
These details confirm that the business has been legally issued an EIN by the IRS, which is a prerequisite for filing taxes, opening a business bank account, hiring employees, and complying with federal regulations.
An example of an EIN verification letter (CP 575 first-page-only) for illustrative purposes only.
Why are EIN verification letters important?
An EIN verification letter isn’t just a tax formality. It’s one of the most trusted documents used to confirm a business’s legitimacy and tax identity. Without it, organizations that want to operate in the U.S. can’t open corporate bank accounts, hire employees, or apply for licenses and permits.
That’s why institutions across industries rely on EIN letters during onboarding and compliance checks.
Here’s how EIN verification letters are used for document verification across specific industries:
- Banking and financial services. Lenders and banks require EIN letters to confirm a business exists before issuing loans, credit, or deposit accounts.
- Payment processors and fintechs. Used to verify the legitimacy of merchants applying for accounts or payment gateways.
- Insurance underwriting. Commercial insurers often request EIN documentation to confirm policyholder identity and reduce fraud risk.
- Government contracting. Agencies check EIN letters to validate that vendors are legally recognized entities before awarding contracts or grants.
Because they come directly from the IRS, EIN verification letters carry strong legal weight, making them a cornerstone of business identity verification and other KYB processes (in the U.S.).
If you’d like to know how fraudsters are creating all these fake EIN verification letters, check out our “Types of fraud” blog to learn more about their tactics.
Threat intel: Template data about fake EIN verification letters
Our Threat Intelligence Unit collects data about template farms which make and distribute fake document templates for fraudulent purposes.
Below, you'll find an infographic containing data about all the fake EIN verification letter templates we've found: their availability, their distributors, the institutions or "issuers" whose documents have been exposed, and how much it costs to buy one.
Interesting note: The small number of issuers could have to do with the overall uniformity of these documents (there's no need for much variety since they all look the same). Their average price is one of the highest in our data set.
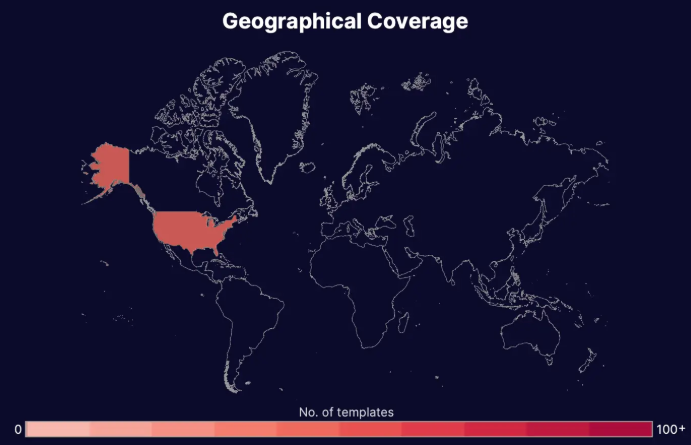
Threat Intel Stats: Employer Identification Number (EIN) Verification Letter
Find more information about the threat these farms pose in our threat intel blog and webinar content.
5 Signs of a forged or fake EIN verification letter
EIN verification letters are deceptively simple documents, which is why fraudsters love them.
Miss a fake, and you could onboard a phantom business, extend credit to a shell company, or approve a contract for an entity that doesn’t legally exist.
Because fraudsters can create documents that closely resemble official IRS notices, simply relying on visual appearance to verify an EIN confirmation letter can be misleading.
If you’d like to detect fake EIN verification letters manually, it’ll require a sharp eye and familiarity with real-world red flags.
Here’s what to watch for:
1. Inconsistent formatting
Authentic IRS-issued EIN letters (CP 575 or 147C) follow strict templates. Deviations in layout or design are among the first giveaways.
- Misplaced IRS logo or seal. The IRS eagle emblem and header should be crisp, not pixelated or shifted.
- Wrong letter code. Every EIN letter is labeled “CP 575” or “147C.” Missing or incorrect codes signal forgery.
- Strange line breaks or text wrapping. Official IRS letters are formatted cleanly; random breaks in the middle of words or awkward wrapping around the page can suggest the document was edited or generated.
- Unusual use of capitalization or bolding. Inconsistent capitalization, excessive bold text, or random changes in emphasis are often signs of a counterfeit template rather than a standardized IRS notice.
- Broken contact information formatting. The IRS Business & Specialty Tax line is always listed the same way; odd spacing or abbreviations are red flags.
2. Incorrect or misleading information
Fraudsters often get core details wrong when attempting to replicate IRS records.
- EIN formatting errors. A valid EIN always follows the pattern XX-XXXXXXX. Variations like missing hyphens or extra digits indicate falsification.
- Business name mismatch. The entity’s legal name must exactly match IRS records; even small spelling errors point to forgery.
- Improper IRS address. Authentic letters reference known IRS centers (Austin, Ogden, Cincinnati). Fake ones may list generic or outdated addresses.
- Suspicious issue dates. A CP 575 cannot be reissued. If you see a “duplicate” CP 575 dated years after formation, it’s fraudulent.
- Responsible party errors. IRS records include a named responsible person; fake letters often skip this or use placeholder names.
3. Bad math and uncharacteristic figures
While EIN letters don’t contain financial calculations, formatting and numbering still follow internal IRS logic. Fakes often stumble here.
- Random notice numbers. Real IRS notices include structured numeric identifiers; arbitrary or inconsistent strings are fabricated.
- Reference numbers that don’t exist. Fake letters may include “case numbers” or “file IDs” not used in real IRS communications.
- Out-of-sequence dates. A letter dated on a weekend or federal holiday is suspicious.
4. EIN letter inconsistencies
The structure of the letter itself offers clear markers when something’s off.
- CP 575 issued twice. The IRS only issues one original CP 575. Any second “copy” is a fake.
- Incorrect IRS terminology. Genuine letters use precise language (“assigned Employer Identification Number”); fakes may say something else like “tax ID approval.”
- Missing IRS contact instructions. Every EIN letter includes a standard helpline and contact hours; their absence suggests tampering.
- Signature or stamp errors. The IRS doesn’t use wet signatures on these letters; if one appears, it’s fabricated.
- Outdated templates. Some fakes reuse letter styles or contact details phased out years ago.
5. Metadata discrepancies
When submitted digitally, metadata can reveal signs of forgery invisible on the surface.
- File created in consumer software. Real IRS PDFs are system-generated; if metadata shows Word, Photoshop, or Canva, it’s fake.
- Creation date vs. issue date mismatch. A letter “issued” March 1 but with a file creation date of March 5 is likely forged.
- Suspicious author tags. Real letters show the IRS as the author; fakes often show a personal name or editing tool.
- Flattened image-based PDFs. Authentic EIN letters are text-selectable. Screenshots or scans rebuilt as images are suspect.
- Region or language anomalies. Metadata set to “French (Canada)” or “en-GB” instead of U.S. English suggests foreign fabrication.
Disclaimer: Catching a fake EIN verification letter by hand is like spotting a forged signature on a blank sheet — it’s possible, but unreliable at scale. Fraudsters today don’t just use Photoshop; they use AI to generate letters that perfectly replicate IRS fonts, headers, and phrasing, generating hundreds of attempts (too many for a human to review).
Manual inspection may help in isolated cases, but it cannot keep pace with modern fraud. That’s why scalable, AI-powered document verification is essential for organizations that handle large volumes of business onboarding and compliance checks.
How to verify an EIN verification letter
Compliance officers, bank underwriters, payment processors, and fraud investigators can verify EIN verification letters either manually or through automated, AI-driven methods.
Manual checks are increasingly unreliable. Fraudsters can download convincing templates or generate near-perfect replicas with AI editing tools, bypassing visual inspection, and challenging even the most experienced risk teams to manage the sheer volume of questionable documents.
AI-based verification, on the other hand, offers scale, speed, and accuracy that manual review cannot. It can analyze layout consistency across thousands of IRS-issued letters, detect metadata manipulation invisible to the naked eye, and flag anomalies in EIN formatting or business names in real time.
That said, manual verification still plays a role in many organizations due to legacy processes or regulatory requirements. If you must review EIN letters manually, use the red flags outlined earlier in this blog and supplement them with official IRS checks (such as calling the IRS Business & Specialty Tax Line or requesting a 147C letter directly). These extra steps won’t scale but can provide assurance in isolated cases.
Manual verification of EIN verification letters
Unlike business registrations or licenses, EIN ownership cannot be publicly verified through an IRS database, leaving yet another blind spot in trying to verify these documents manually. You would have to contact the IRS directly.
Still, if you’re reviewing an EIN letter manually, start by applying the fraud signs listed above. Then consider these additional methods:
- Contact the IRS directly. Call the IRS Business & Specialty Tax line (+1-800-829-4933) to confirm whether an EIN is valid and tied to the business in question, or visit their website.
- Request a 147C letter. If a company claims to have lost its CP 575, the IRS can issue a 147C letter to re-confirm its EIN. Fraudsters can’t generate a legitimate one on demand.
- Check the business in state registries. Verify that the company’s legal name and EIN match what appears in the Secretary of State or corporate registry databases.
- Cross-reference against tax filings. EINs are used on W-2s, 1099s, and other filings. Comparing the EIN across multiple documents can reveal inconsistencies.
- Confirm with banking or licensing partners. Banks and licensing agencies often require EIN validation. If their records don’t match the submitted letter, it’s likely fake.
Keep in mind: Manual checks might work for smaller volumes, but they’re inefficient and prone to error. With fake EIN letters spreading rapidly online, relying on one-off calls or spot checks won’t scale in high-risk industries (or spot invisible-to-the-eye red flags).
Using AI and machine learning to spot fake EIN verification letters
AI-powered verification takes EIN fraud detection far beyond manual checks.
AI systems learn the precise structure, metadata patterns, and formatting, and submission behaviors that real documents follow. That allows them to detect subtle forgeries instantly.
Benefits of AI in EIN verification include:
- Rapid large-scale analysis. Review hundreds or thousands of EIN letters automatically, with no bottlenecks.
- Deep structural analysis. Goes beyond surface appearance by examining how the IRS letter was digitally constructed (layers, object placement, and generation logic)
- Real-time anomaly flagging. Spot mismatched EIN patterns, misspelled business names, or suspicious formatting immediately.
- Hundreds of specialized fraud checks. Leverages a library of hundreds of specialized detectors (500+) to spot patterns, inconsistencies, and tampering techniques that no manual reviewer could realistically catch.
- Reduced false positives. AI learns from new fraud attempts, improving detection accuracy over time.
Automation vs. AI
Automation or rules-based systems can check if fields are present (like “business name” or “EIN”) and confirm basic formatting rules. That helps filter out obvious fakes, but it can’t adapt when fraudsters evolve their templates.
AI learns dynamically. It doesn’t just check that an EIN field exists — it validates whether that EIN follows IRS logic, aligns with metadata, and matches known fraud signatures. In short: automation applies rules, AI applies reasoning.
Conclusion
Fake EIN verification letters are more than a nuisance — they’re a gateway for fraudsters to impersonate businesses, secure credit, and infiltrate financial systems.
With free templates and AI-driven forgeries flooding the web in 2026, manual checks are no longer enough. If your organization still relies only on human reviewers, you risk missing sophisticated scams and drowning under document volumes and mass assaults.
The safest path forward is adopting AI-powered document fraud prevention.
Resistant AI’s document fraud detection software digs deeper to uncover hidden editing patterns, detect tampered files, and flag anomalies that no manual review would catch. The result? Faster onboarding, lower fraud losses, and a stronger defense against synthetic business identities.
If your organization depends on EIN verification letters for trust, you can’t afford outdated processes. AI provides the scale and precision fraudsters can’t match.
Scroll down to book a demo.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Hungry for more fake EIN verification letter content? Here are some of the most frequently asked fake EIN letter questions from around the web.
How to spot EIN verification letters with AI?
AI can detect fake EIN verification letters by analyzing formatting, metadata, and content against thousands of genuine IRS-issued CP 575 and 147C templates. It flags anomalies like nonstandard EIN formats, inconsistent metadata timestamps, or fonts that don’t match IRS system-generated letters — details that human reviewers often miss.
What’s the difference between an EIN verification letter, a W-9, and a business license?
While all three are used in business verification, EIN verification letters, W-9s, and business licenses serve very different purposes. One confirms a company’s tax ID with the IRS, another provides taxpayer details to third parties, and the last grants legal permission to operate a business.
- EIN verification letter: Confirms a business’s official IRS-assigned Employer Identification Number (EIN)
- Issued by: Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
-
- Characteristics:
- Issued as CP 575 (initial notice) or 147C (replacement).
- Contains EIN, business name, and IRS contact details
- Characteristics:
- W-9 (Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification): Provides taxpayer identification info for reporting purposes (like issuing 1099s)
- Issued by: Self-completed by businesses or individuals and submitted to payers
-
- Characteristics:
- Completed by the taxpayer, not the IRS
- No legal verification or confirmation of EIN validity
- Characteristics:
- Business license: Grants legal authorization to operate within a jurisdiction.
- Issued by: City, county, or state government agencies.
- Characteristics:
- Lists business name type of activity permitted, license number, and expiration date.
- Issued by: City, county, or state government agencies.
Is there software to detect fake EIN verification letters?
Yes. Resistant AI offers advanced document fraud detection software that can authenticate EIN verification letters by checking structural layout, analyzing metadata, and cross-referencing details against IRS standards.
Who needs to check for fake EIN verification letters?
Within organizations, specific roles are tasked with preventing fraud, ensuring compliance, and protecting financial integrity. Here are the professionals most responsible for reviewing EIN verification letters, and why:
-
Compliance officers. Verify EIN letters during Know Your Business (KYB) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks to ensure that the entity is legitimate and tax-registered with the IRS.
-
Risk managers. Assess the authenticity of EIN documentation to prevent onboarding shell companies or fraudulent vendors that could create financial or regulatory exposure.
-
Loan underwriters. Use EIN letters to confirm that business applicants have a valid IRS-issued tax ID before extending credit, loans, or mortgages.
-
Procurement officers. Review EIN letters when vetting new suppliers or contractors, making sure vendors are real, tax-compliant businesses.
-
Insurance underwriters. Check EIN letters to confirm that applicants for commercial insurance policies represent legitimate entities with valid tax status.
-
Accounts payable teams. Validate EIN letters when setting up new vendors in payment systems, helping avoid payouts to fraudulent or non-existent companies.
Is making a fake EIN verification letter illegal?
Absolutely. Creating or using a fake IRS EIN verification letter is considered federal fraud in the U.S. Under 18 U.S.C. § 1001, providing false statements or documents to a federal agency carries heavy penalties, including fines and imprisonment. Using one in financial or contractual settings can also result in wire fraud or conspiracy charges.
How do I get a copy of my EIN verification letter (147C)?
Call the IRS Business & Specialty Tax Line at 800-829-4933 (Mon–Fri, 7 a.m.–7 p.m. local time). An IRS agent can issue a Letter 147C (EIN previously assigned) to confirm your EIN and send it by fax or mail after identity proofing of an authorized party.
Can the IRS reissue a CP 575?
No. A CP 575 is system-generated only when the EIN is first assigned; it isn’t reissued. If the original is lost, the IRS provides a 147C as the official replacement/verification.
Can I verify an EIN online?
There’s no public “search all EINs” tool. However, authorized payers can validate name/TIN combinations through the IRS TIN Matching e-Services, and the IRS does offer public search only for tax-exempt organizations via the Exempt Organization Search.