How to spot fake bank statements


When it comes to bank statement fraud in 2026, there’s a ripple effect that extends far beyond the immediate parties involved, impacting the broader financial landscape.
On top of that, it's easier now than ever to produce fake bank statements. Public domains with millions of templates are only a click away.
Being one of the most commonly used documents for income verifications, bank statements are a vital to institutions during customer onboarding and loan approval processes. Detecting document fraud in bank statements is imperative.
Read on to learn what a bank statement is, why it's important, how to identify a fake bank statement, and how AI-powered verification solution can help spot them automatically.
Check out our "How to spot fake documents" blog to learn about more common document forgeries.
What is a bank statement?
A bank statement is an official summary issued by a financial institution that details all transactions within a specific account over a defined period (typically one month).
It serves as a record of account activity and provides a comprehensive view of deposits, withdrawals, charges, and balances.
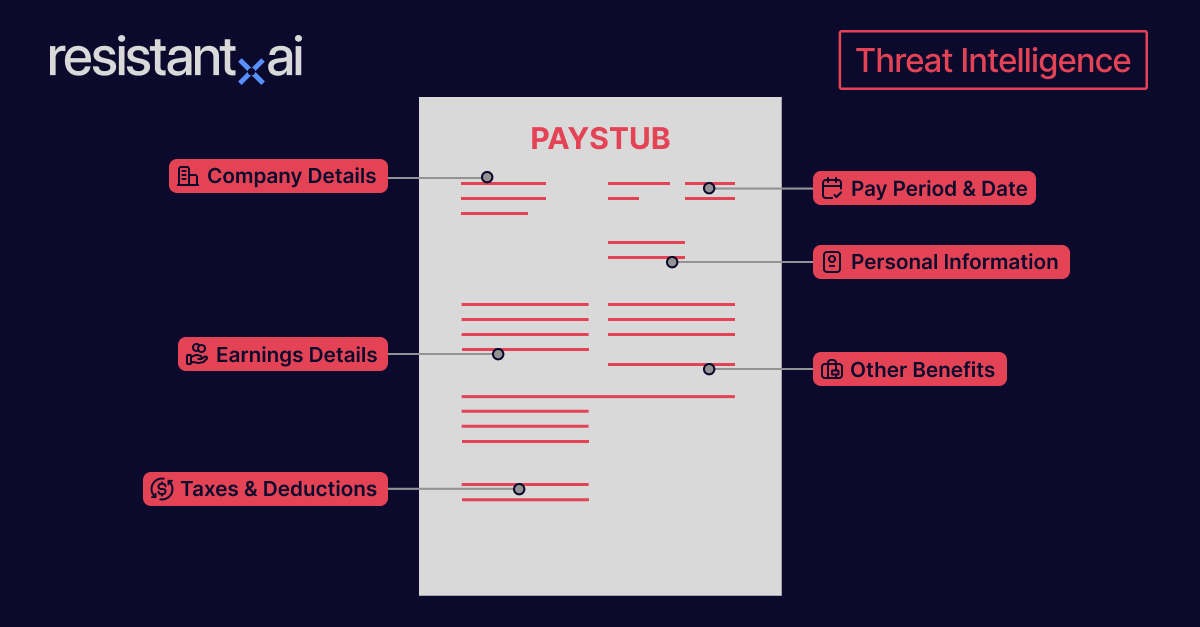
They typically contain:
-
Account holder information. Name and address, account number (partially masked in some cases).
-
Statement period. Start and end date of the reporting period.
-
Bank information. Bank name, logo, contact details, and branch information.
-
Opening and closing balances. Balance at the start and end of the statement period.
-
Transaction details. Date of each transaction, description or merchant name, amount debited or credited, running balance after each transaction.
-
Deposits and credits. Direct deposits (e.g., salary, refunds), transfers from other accounts, interest earned (if applicable).
-
Withdrawals and debits. ATM withdrawals, debit card purchases, online transfers or bill payments, bank fees or service charges.
-
Summary section. Total deposits, withdrawals, and fees for the period.
-
Additional notes or disclosures. Bank policies, changes in terms, or fraud alerts
These contents help document checkers assess an individual’s or entity’s financial activity, income consistency, and account authenticity.

An example of an invoice for illustrative purposes only
What is bank statement fraud?
Bank statement fraud is a form of financial fraud in which bank records (including statements and balances) are manipulated or fabricated.
It poses a significant threat to both the integrity and reliability of financial transactions. The terms "fraudulent bank statements" or "fake bank statements" are also used to describe this type of fraud. Bank statement scams can take on several forms, each of which comes with its unique methods and implications.
The ability to discern the authenticity of a bank statement for both businesses and financial institutions, which have always relied heavily on these documents for an array of financial decisions and operations. For this reason, the increasing prevalence of financial fraud—particularly bank statement fraud—has become a pressing issue.
Why are bank statements important?
Bank statements are used for personal financial management, account reconciliation, and as documentation for income or asset verification in financial processes such as loan applications or audits.
Businesses and financial institutions have always relied heavily on these documents for this array of financial decisions and operations, making the ability to discern their authenticity essential.
Some of the processes that involve bank statement scam detection include:
-
Loan underwriting. Lenders analyze applicant bank statements to assess spending behavior, savings history, and income deposits. This helps them evaluate creditworthiness and reduce exposure to high-risk borrowers.
-
Immigration and visa processing. Consulates and immigration authorities require verified bank statements to demonstrate proof of financial means, helping prevent fraudulent or unsupported visa applications.
-
Financial aid and scholarship applications. Educational institutions and grant committees validate bank statements to confirm need-based eligibility and prevent fraudulent claims of financial hardship.
-
Business credit applications. Lenders and leasing companies request company bank statements to verify cash flow, gauge solvency, and prevent misrepresentation in commercial credit applications.
Bank statements offer real-time insight into actual financial activity. Their standardized format, traceable transaction history, and direct link to a regulated financial institution make them one of the most trusted sources for confirming income, liquidity, and spending behavior.
In 2026, more banks have started rolling out dynamic statement elements (like rotating transaction IDs, embedded verification hashes, or issuer-specific export fingerprints) specifically to combat fake bank statement fraud.
Ironically, this has created a new red flag: fraudsters are still submitting “perfect-looking” statements that lack these newer, bank-specific structural markers, making older-style templates easier to spot at scale.
If you’d like to know how fraudsters are creating all these fake bank statements, check out our “Types of fraud” blog to learn more about their tactics.
Why do people commit bank statement fraud?
Bank statement fraud is driven by an array of various motivations:
-
Loan and credit access. Individuals often commit this fraud to gain access to loans or credit by misrepresenting their proof of income or solvency, thereby securing higher loan amounts or more favorable interest rates.
-
Evading taxes. Tax evasion is another common goal, where individuals under-report their income on bank statements to reduce their taxable income.
-
Rental and job requirements. Individuals may resort to bank statement fraud to meet personal needs, such as securing a lease on an apartment or demonstrating their proof of income and financial viability for a job.
-
Identity theft. In cases of identity theft, a stolen ID card alone may not suffice to open an account; hence, perpetrators may also forge bank statements and other documents to authenticate their false identity.
-
Business transactions and partnerships. Businesses aren’t immune to committing bank statement fraud either—they might alter bank statements to misrepresent their financial health in an aim to secure loans, facilitate transactions, or attract partnerships under false pretenses.
-
Money laundering. A more sinister motive is money laundering, where bank statement fraud is used to conceal illicit financial activities, including hiding risky counterparties or unusual transactions during financial audits.
Threat intel: Template data about fake bank statements
Our Threat Intelligence Unit collects data about template farms which make and distribute fake document templates for fraudulent purposes.
Below, you'll find an infographic containing data about all the fake bank statement templates we've found: their availability, their distributors, the institutions or "issuers" whose documents have been exposed, and how much it costs to buy one.
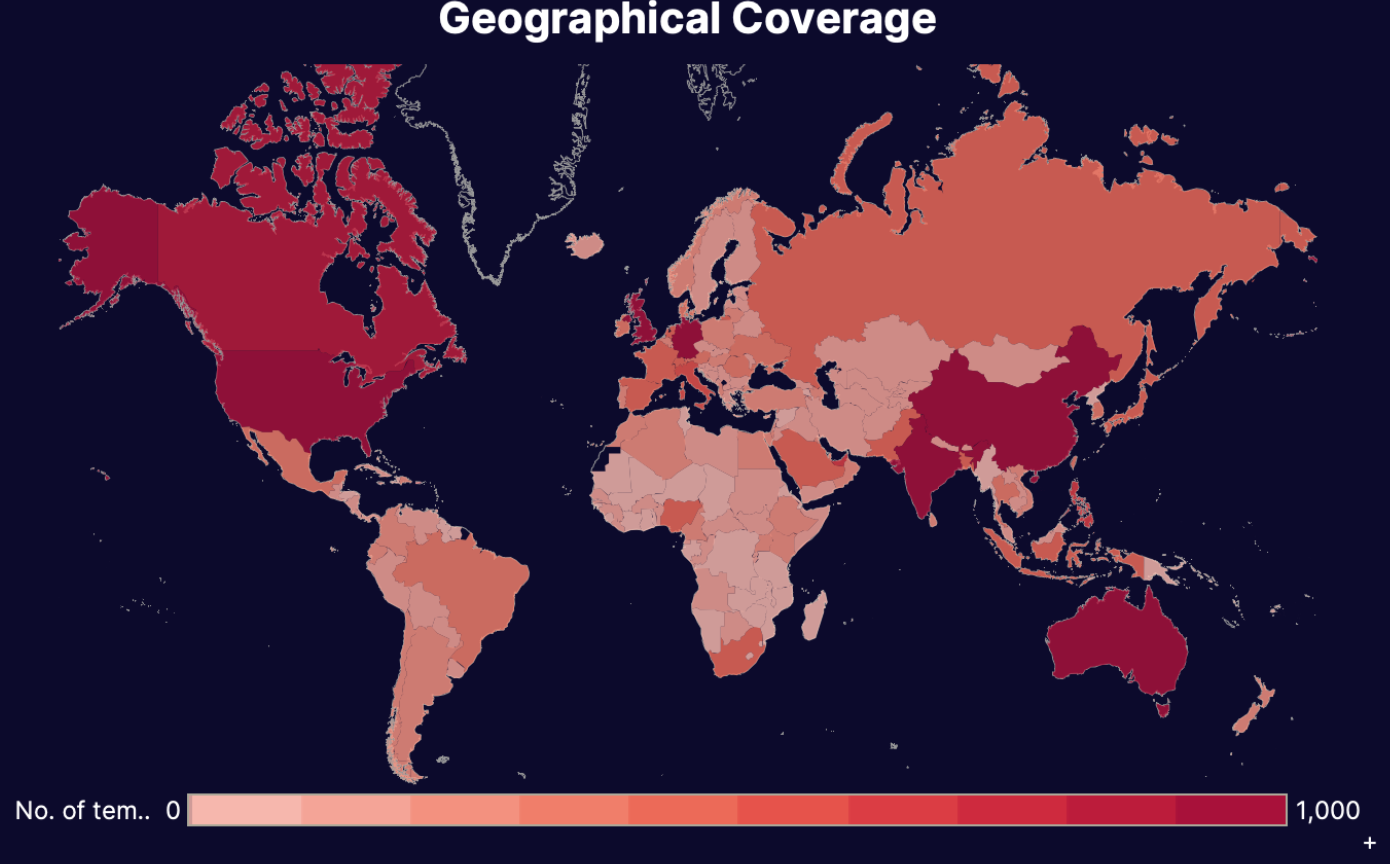
Threat Intel Stats: Bank Statements
Find more information about the threat these farms pose in our threat intel blog and webinar content.
What are the types of bank statement fraud?
Fraudsters have become increasingly sophisticated in their methods, and have several different methods for generating bank statement fakes.
Here are a few specific types of bank statement scam:
-
Phony bank statements. Fraudsters fabricate bank statements entirely from scratch. These documents are entirely illegitimate and can feature fictitious account balances, transactions, and personal details.
-
Manipulating balances. Fraudsters alter the figures on legitimate bank statements by inflating or deflating account balances. This creates the appearance of greater financial stability or hides improper financial activities.
-
Altering transactions. Frausters change specific details of transactions on a bank statement, such as dates, amounts, or descriptions. Such alterations can conceal unauthorized transactions or create a misleading financial history.
5 Signs of a fake or forged bank statement
If you’re validating bank statements manually, it’s important to look out for both formatting issues and data inconsistencies that signal potential tampering.
Fraudsters often alter balances, create fake deposits, or forge entire documents to meet requirements in loan applications, tenant screening, or financial aid requests.
Here are the most common indicators of bank statement fraud:
1. Formatting anomalies
Legitimate bank statements follow consistent templates defined by each financial institution. Forgeries often show signs of manual editing or template misuse, such as:
-
Mismatched fonts. Different font types or sizes for balances, names, or transaction labels.
-
Misaligned columns. Deposits, withdrawals, and running balances are uneven or don't follow a consistent grid.
-
Blurry or pixelated logos. Bank logos appear scanned, low resolution, or copied from another document.
-
Improper file format. Submitted in Word, Excel, or editable PDFs instead of scanned or password-protected PDFs.
-
Fake web portal designs. Screenshots or mockups of online banking pages instead of downloadable statements.
2. Inconsistent account details
Basic account information should be consistent across all pages and match other submitted documents:
-
Different account numbers on different pages of the same statement.
-
Account holder name doesn’t match the name used on the application or ID documents.
-
Incorrect bank branch or contact info that doesn't exist or doesn’t match the claimed bank's records.
3. Transaction irregularities
Genuine bank statements include a clear, timestamped record of daily financial activity. Red flags in transaction history include:
-
Perfectly rounded or repeated deposits. Multiple identical salary payments (e.g., exactly $5,000 every month) with no variation.
-
Unusual activity patterns. No utility bills, groceries, or standard monthly expenses, especially for personal accounts.
-
Backdated transactions that don't match public holidays or weekends when banks are closed.
-
Inconsistent running balances. Balances that don’t add up after deposits or withdrawals.
-
Deposit descriptions that don’t match the stated employer (e.g., vague “credit” or “incoming transfer” instead of “Company X Payroll”).
4. Metadata and file origin discrepancies
Even well-formatted statements can be exposed through digital forensic checks:
-
Document created in Word or Photoshop. Metadata shows editing software not used by banks.
-
Recent creation date for old statements. A statement for January was created just days before submission.
-
No encryption or digital watermark. Many banks issue secured PDFs with embedded digital signatures or verification codes.
5. Misuse in specific processes
Bank statements forged for particular use cases often fail to meet industry-specific expectations:
-
Loan underwriting. Claimed income on bank statement doesn’t match submitted pay stubs or W-2s.
-
Tenant screening. Rent payments shown going to the landlord don’t match the lease or landlord’s name.
-
Financial aid. Statement shows low balances, but no recent expenses or transaction activity to support financial hardship claims.
Disclaimer: Spotting these red flags manually is not only time-consuming but also unreliable at scale. As fraud tactics become more sophisticated, using AI-powered document verification is essential for consistently detecting forged bank statements with speed and accuracy.
How can you prevent bank statement fraud?
By implementing strategic measures, individuals, businesses, and financial institutions can significantly reduce bank statement fraud.
Some key strategies for preventing bank statement fraud include: carrying out regular reviews and systematic vigilance, education and awareness, and making use of advanced fraud detection solutions.
Conduct regular reviews and systematic vigilance
The cornerstone of preventing bank statement fraud is the regular, meticulous review of financial statements. This practice allows for early detection of discrepancies or anomalies that might indicate fraudulent activity.
Businesses and financial institutions should incorporate regular audits of financial documents into their routine processes. These audits can help identify inconsistencies that might otherwise go undetected in day-to-day operations.
This kind of systematic vigilance isn’t just about spotting anomalies. It’s about understanding the usual patterns of one’s financial activities — the ability to recognize what constitutes normal transactional behavior, enabling the swifter identification of any irregularities.
Prioritize education and awareness
Education and awareness give your teams the tools they need to combat bank statement fraud. Conduct regular communication, workshops, and provide resources that help recognize and respond to potential fraud attempts.
Everyone who deals with bank statements should be able to recognize the signs of bank statement fraud. Trains could cover: the various forms of fraud, how to verify the authenticity of financial documents, and the procedures to follow whenever fraud is suspected.
Use AI and machine learning
In the contemporary financial security landscape, the integration of AI and machine learning has been a game-changer in protecting businesses and financial institutions against bank statement fraud. These technologies bring a high level of sophistication and analytical aptitude to the table, serving as essential tools in the ongoing battle against this kind of fraud.
The dynamic nature of these technologies is one of their most remarkable features. As they’re exposed to more data, they continually refine and enhance their detection capabilities. This adaptability is crucial in staying ahead of sophisticated fraudsters who are constantly evolving their methods.
How to Verify Bank Statements
Verifying bank statements is a critical part of processes like loan underwriting, tenant screening, compliance checks, and fraud prevention.
Loan underwriters, tenant screening agents, property managers, and compliance officers have two primary methods for validating these documents: manual inspection and AI-driven verification software.
While manual checks are still in use, we strongly recommend using AI and machine learning solutions for faster, more accurate, and scalable detection. Especially as fraudsters adopt more sophisticated techniques.
Manual verification of bank statements
Manual checks involve carefully reviewing the contents and structure of the bank statement to spot signs of forgery or inconsistency. This includes:
-
Cross-checking personal information. Verifying that the name, address, and account number match the applicant’s other documentation.
-
Assessing transaction consistency. Looking for regular deposits, everyday expenses, and a logical flow of account activity (e.g., running balances that correctly reflect debits and credits).
-
Analyzing formatting and design. Ensuring the bank’s logo, fonts, and layout align with known templates from the issuing institution.
-
Comparing declared income. Matching transaction records (e.g., payroll deposits) with other documents like pay stubs or W-2 forms.
-
Spotting unusual patterns. Identifying red flags such as identical deposits every month, strange date gaps, or inconsistent statement lengths.
Keep in mind: While manual verification may catch obvious errors or outdated forgeries, it’s slow, inconsistent, and heavily reliant on human judgment.
Many modern forgeries are nearly indistinguishable to the naked eye, especially when fraudsters use real templates, cloned logos, or AI-assisted document editing.
Additionally, manual reviews don't scale well and often miss subtle metadata anomalies or file manipulation traces—leaving businesses exposed to unnecessary risk.
Using AI and machine learning to spot fake bank statements
AI-powered verification software automates the analysis of bank statements using machine learning models trained on thousands of real and fraudulent examples.
These systems examine document structure, formatting patterns, transaction behaviors, metadata, and cross-document consistency to detect manipulation at a forensic level.
Key advantages include:
-
Speed and scalability. Instantly process and analyze hundreds of documents in minutes, freeing up compliance and risk teams.
-
Advanced fraud detection. Identify inconsistencies in running balances, duplicated transaction patterns, or discrepancies in employer deposits.
-
Metadata forensics. Surface signs of tampering at the file level (e.g., edited with non-bank software, backdated creation).
-
Cross-document validation. Compare data points across submitted documents (e.g., pay stubs, ID, lease agreements) to flag mismatches and spot serial fraud.
-
Custom rules and risk scoring. Adapt to evolving fraud tactics with flexible thresholds and scoring mechanisms for high-risk documents.
AI verification not only improves accuracy but also helps institutions scale fraud prevention without slowing down operations — making it the superior solution for verifying bank statements in high-stakes environments.
Conclusion
Bank statement fraud get more sophisticated by the day. Relying on manual checks alone leaves your organization exposed.
With Resistant AI, you can automate document verification, catch subtle signs of tampering, and scale your fraud prevention efforts with confidence.
Scroll down and book a demo to see how our solution works in real time and start protecting your workflows from day one.
Frequently asked question (FAQ)
Hungry for more fake bank statement content? Here are some of the most frequently asked fake bank statement questions from around the web.
What’s the difference between a bank statement and a bank letter?
These two documents are often confused because they’re both issued by banks and used for verification, but they serve very different purposes in financial and compliance workflows.
Bank statement: A detailed record of financial activity over a specific time period.
-
Issued by:
-
The account holder’s bank, typically through online banking portals or mailed statements.
-
-
Characteristics:
-
Includes transaction history: deposits, withdrawals, fees, and running balances.
-
Covers a defined statement period (usually monthly).
-
Used for: Income verification, loan underwriting, tenant screening, and compliance checks.
-
Presented in PDF or physical format, often with pagination, bank logos, and customer details.
-
Bank letter (also called a bank reference letter or proof of account): A formal confirmation that an account exists and is in good standing.
-
Issued by:
-
A bank representative, typically upon request by the account holder.
-
-
Characteristics:
-
Includes limited information: account holder name, account type, open date, and sometimes average balance.
-
Used for: Immigration applications, business registrations, or proof of relationship with a bank.
-
Usually formatted as a one-page letter on official letterhead, signed and dated by a bank official.
-
Is making a fake bank statement illegal?
Yes, creating or submitting a fake bank statement is considered fraud and is illegal in most jurisdictions.
It can lead to serious consequences including criminal charges, fines, civil liability, and denial of loans, housing, or visas, depending on the intent and context in which the fake document is used.
What is the impact of bank statement fraud?
Bank statement fraud can have profound impacts on both businesses and financial institutions and often leads to consequences that extend far beyond the initial deception.
When businesses fall victim to bank statement fraud, they may inadvertently make decisions that compromise their integrity and financial health.
For example, by relying on fraudulent financial documents, companies might enter into partnerships with entities that don’t have the financial stability or ethical standing that they claim to have. This can lead to significant financial losses or entanglements in legal disputes that can tarnish the company's reputation and erode stakeholder trust.
Businesses may also base critical investment decisions on the distorted financial reality presented by fraudulent bank statements, allocating resources to ventures that aren’t as viable or profitable as they appear.
Similarly, the hiring process can be compromised if candidates provide fraudulent financial documents to falsify or exaggerate their financial stability, leading to the recruitment of individuals who may not be best suited for the roles that they’re given.
For financial institutions, the stakes are equally high: loans can be extended based on fraudulent financial information, leading to higher default rates and financial losses.
Being associated with fraudulent activities (even unknowingly) can also severely damage a financial institution's reputation, undermining customer trust and potentially leading to a loss of business. In the worst cases, it might attract regulatory scrutiny and legal consequences.
How do you carry out an anti-fraud technical document analysis on bank statements?
Technical analysis plays a pivotal role in detecting bank statement fraud. This involves a deeper examination of the document's metadata and history.
- Metadata discrepancies: Metadata (such as the creation date or the software used to generate the document) can reveal alterations that have been made.
- File history examination: An analysis of the document’s edit history can uncover unauthorized modifications.
How can you detect fraudulent bank statement document templates?
Fraud templates are customizable documents that make committing document fraud far more accessible. No forgery expertise necessary.
These template user rely on the work others have done to generate fake bank statements, making minimal changes to one aspect of the document (like names, account numbers, or addresses) while keeping other parts untouched (such as transactional information, dates, and amounts).
In the more benign form, individuals might rely on these documents to qualify for financial services they normally wouldn’t — a form of crowd-sourced first-party fraud.
At their most extreme, these templates can be combined with leaked, stolen, synthetic, or fabricated identities to produce bank statements on a large scale and submitted into account or loan applications through automated systems by organized crime rings (serial fraud).
So, how can you spot fraud templates?
Institutions must meticulously examine bank statements for similarities or repeating patterns and characteristics that defy statistical probability.
Because these changes are small and easily overlooked, identifying fraud of this nature can be nearly impossible for humans alone. To spot template bank statement fraud you need an AI-powered solution.
Is there software to detect fake bank statements?
Holistic fraud detection systems take a comprehensive approach to fraud prevention.
Resistant AI's document fraud detection analyzes over 500 characteristics that might escape the human eye, scrutinizing aspects that go beyond obvious details like the type of document, the authorship, and the software used in its creation.
This deep analysis can detect even the slightest alterations or inconsistencies that could indicate tampering or forgery.
That scrutiny also extends to image analysis to detect anomalies such as inconsistencies in resolution or signs of digital manipulation.
Beyond the individual document analysis, our system also compares all incoming documents to find signs of document reuse, template farms, or other serial document fraud threats.
This level of detail ensures a comprehensive and reliable assessment of each document, making these systems invaluable allies for risk-minded organizations.
Who needs to check bank statements for forgery?
Bank statement fraud isn’t just a problem for banks. A wide range of industries and teams rely on bank statements to verify identity, income, or financial behavior. That means they’re also vulnerable to forgery — especially as synthetic document fraud becomes more accessible through digital tools and generative AI.
-
Lenders. Whether it’s a payday lender or a mortgage provider, underwriters rely on submitted statements to assess risk and make decisions.
-
Landlords and tenant screening services. Regularly review bank statements to verify income or financial responsibility.
-
Fintech platforms. Often require document-based onboarding.
-
Insurance companies. May request bank statements as part of a claims process, particularly in cases of fraud investigations.
-
Employers and HR teams. In contract work scenarios where proof of income or prior employment is required.