
You might be interested in






The skies have never been more crowded. In 2025, airlines are expected to carry a record 5.2 billion passengers, a 6.7% increase from 2024 — the first time ever surpassing the 5 billion mark. That number will only continue to grow now that we're in 2026.
At the same time, digital ticketing has become the overwhelmingly dominant norm: 85% of airline bookings are now expected to be completed through digital channels, with the majority of flight documents delivered via email or mobile apps.
As travel picks up, and the medium becomes predominantly digital, it opens the flood gates to anyone (from seasoned fraudsters to disgruntled passengers) to take advantage.
Fueled by generative AI, online document templates, and accessible forgery tools, criminals now effortlessly fabricate convincing flight tickets. These fraudulent files can manipulate travel insurance claims, exploit refund processes, or deceive immigration officers, bypassing risk teams and costing institutions millions.
Worse yet, modern fakes are harder to detect manually than ever before. Understanding the anatomy of real flight documents (and recognizing telltale signs of digital tampering) is essential to maintaining the integrity of your verification processes.
Read on to learn what flight tickets are, why they're crucial for travel verification, and how advanced AI can detect these fakes automatically.
For more insights on document fraud, check out our “How to spot fake documents” blog.
Flight documents (flight tickets, e-tickets, boarding passes) verify reservation status and travel details at different stages of a passenger's journey.
While often confused with boarding passes, flight tickets confirm purchase and reservation, while boarding passes enable physical movement through airport security and onto the flight.
The terms "flight ticket" and "e-ticket" are also often confused, but generally refer to the same thing today. Historically, airlines issued physical paper tickets, but these have been replaced entirely by digital versions called e-tickets. An e-ticket is essentially a digital confirmation sent via email or available in a travel app that provides proof of purchase and reservation.
Flight ticket contents typically include:
Passengers use e-tickets primarily during booking, reimbursement processes, and for immigration or visa purposes before travel. Although travelers might print e-tickets for convenience, physical paper tickets have become almost obsolete.
Flight tickets confirm a passenger’s right to board a specific flight, provide accountability for the airline’s services, and can be used as proof of travel. An example of a flight ticket for illustrative purposes only
An example of a flight ticket for illustrative purposes only
Flight tickets are widely used as proof-of-travel for visa applications, expense reports, and insurance claims. Fake tickets are used to make fraudulent claims, bypass application processes and create faulty expense reports.
Here's how various industries rely on flight tickets for document verification:
This blog is one of our most frequently visited thanks to the growing reliance on flight tickets for company reimbursement programs. Many companies will cover flight costs and only ask for a flight ticket, airline confirmation, or boarding pass as evidence.
Unfortunately, in our experience, templates for these documents are widely available and present a uniquely easy opportunity for employees to scam their companies.
If you’d like to know how fraudsters are creating all these fake flight tickets, check out our “Types of fraud” blog to learn more about their tactics.
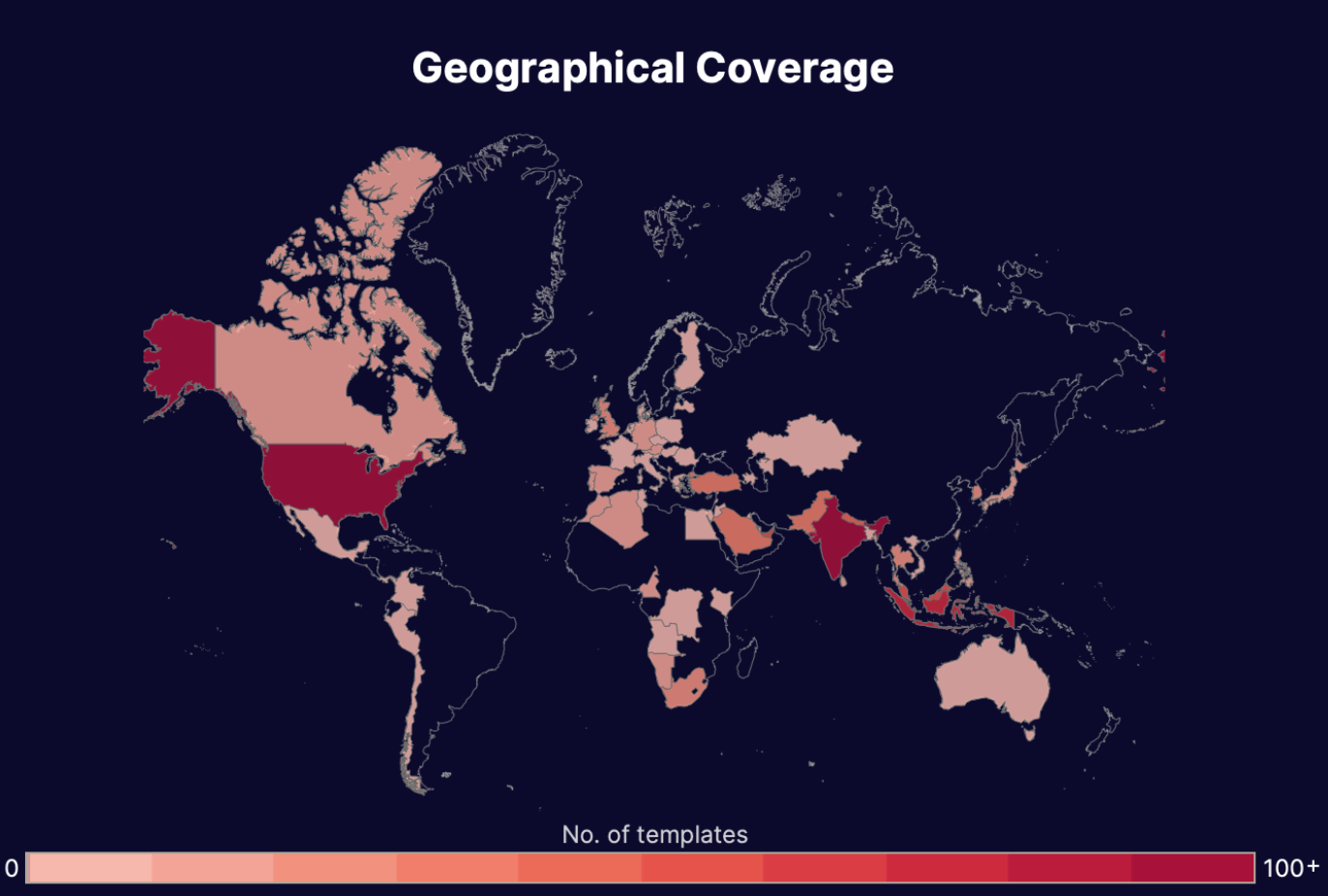
Our Threat Intelligence Unit collects data about template farms which make and distribute fake document templates for fraudulent purposes.
Below, you'll find an infographic containing data about all the fake flight ticket templates we've found: their availability, their distributors, the institutions or "issuers" whose documents have been exposed, and how much it costs to buy one.
Interesting note: Flight tickets are one of the cheapest document templates to purchase we've come across in our research.
Find more information about the threat these farms pose in our threat intel blog and webinar content.
Identifying fake flight tickets manually demands attention to detail and familiarity with airline-specific formatting. Fraudsters can replicate airline branding and layouts convincingly (or edit existing documents), making visual verification increasingly challenging.
Here’s some easy-to-spot red flags in fake flight tickets:
Authentic airline documents follow rigid formatting rules. Deviations in structure or appearance can indicate tampering or forgery.
Forged flight tickets often contain inaccuracies due to lack of knowledge or careless mistakes.
Errors in financial or numerical information reveal document forgeries, especially when scammers misunderstand airline pricing logic.
Airlines carefully control ticket issuance, leaving clear formatting fingerprints that fraudsters fail to replicate.
Digital versions of flight documents often contain hidden clues of forgery in their file metadata.
Disclaimer: Manual checks alone won’t stop today’s AI-powered forgeries. Scalable, AI-driven verification solutions are now essential, flagging anomalies hidden in document structures and metadata that human eyes simply miss.
Insurance underwriters, border control agents, and fraud investigators can verify flight tickets manually or use AI-powered automation.
Manual verification is increasingly inadequate because fraud has gotten incredibly easy and accessible in 2026. Replicable templates are only a download away and Gen AI image generation can produce near-perfect results. Precision beyond human fraud detection is only a click away and even the most seasoned risk teams can’t deal with the sheer volume of average Joe fraud attacks.
AI-powered automation, by contrast, is faster, more scalable, and able to identify subtle anomalies and digital manipulations that manual reviewers often miss.
Still, many roles continue to rely heavily on manual verification due to existing workflows or regulatory constraints. While we recommend upgrading your verification process, if you’re still conducting manual reviews, keep these tips in mind:
Cross-checking your documents against the clear signs of flight document fraud mentioned above is a good place to start. To verify authenticity further:
Keep in mind: While manual verification helps catch obvious discrepancies, it can’t efficiently detect sophisticated forgeries or modern fraud tactics. Cross checking or verifying every ticket by hand would take too long and wouldn’t be scalable for growing businesses. With the best verification systems limited to airlines and law enforcement, the extent of the verification is also limited.
AI significantly enhances flight document verification by analyzing subtle indicators invisible to human reviewers. Rather than reading document content, AI focuses on structural and digital patterns that expose forgery.
Benefits of AI in spotting flight document scams:
Automation works well for repetitive rule-based checks. For example, confirming that a boarding pass barcode is present or that a ticket number field is filled. But it breaks down when facing complex, context-sensitive fraud.
It follows hard-coded rules such as “seat number must be numeric” or “airline logo must appear in the upper-right corner.” While effective for surface-level checks, automation fails when fraudsters accurately replicate airline layouts while subtly manipulating passenger details or flight information.
Machine learning models, on the other hand, understand the full structure and context of a document. They detect when a boarding pass timestamp doesn’t match real airline schedules, or when a ticket number deviates slightly from established airline numbering patterns. AI checks fields AND reasons across them, combining visual, textual, and digital metadata cues.
Fake flight tickets can lead to costly chargebacks, insurance fraud, and onboarding the wrong customers, partners, or employees. For businesses that rely on verifying travel documents (such as insurers, travel agencies, and event organizers) even small numbers of convincing fakes can disrupt operations and create financial losses.
Resistant documents helps prevent this by using advanced AI-driven document analysis to detect hidden anomalies in layout, structure, and metadata that human review or simple template matching can miss. This means faster, more accurate verification, fewer manual checks, and protection against increasingly well-made fraudulent tickets.
Want to see how it works in practice? Scroll down to book a demo.
Hungry for more fake flight ticket content? Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about fake flight tickets from around the web.
Resistant AI uses advanced machine learning models to detect fake flight tickets. By analyzing structural layouts, visual patterns, and subtle digital anomalies invisible to the human eye, Resistant AI flags suspicious documents instantly. Trained on millions of authentic travel documents, our system identifies forged timestamps, mismatched itinerary details, altered metadata, and signs of generative AI manipulation—stopping fraud before it impacts your business.
Flight tickets, boarding passes, and e-ticket confirmations are distinct documents used at different stages of travel verification. While flight tickets and e-tickets are basically the same thing in 2026, boarding passes are used at a different stage of this journey:
Flight ticket (e-ticket): Proof of reservation and payment confirming a traveler’s right to board a specific flight.
Boarding pass: Authorization to enter security checkpoints and board the aircraft.
These five roles are particularly vulnerable to flight ticket fraud:
Yes. Creating, altering, or using forged flight tickets is illegal in virtually every jurisdiction. Penalties include fines, imprisonment, travel bans, or severe immigration consequences depending on the country and severity of the offense.
Fake flight documents are commonly exploited for:
While highly sophisticated fakes may initially deceive visual checks, legitimate airport security protocols, such as barcode scanning at checkpoints, significantly reduce the effectiveness of forged flight tickets. Flight logs make them close to impossible to use for illegitimate travel.
Instead, fraudsters typically use fakes for financial or identity fraud outside airport security contexts.


