Nearly ⅓ of UK businesses fell victim to invoice fraud in 2023-2024.
But this isn’t just a nightmare for UK businesses, it’s also a cautionary tale for any trade finance business about how easy it is to tamper with invoices through basic PDF edits—either to falsify, forge or fake invoices to obtain illicit funds.
Read on to learn what an invoice is, how they're being faked, how to identify a fake, and how AI-powered verification solutions can spot them automatically.
Check out our "How to spot fake documents" blog to learn about more common document forgeries.
What is an invoice?
An invoice is a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer that itemizes and records a transaction. It outlines the details of goods delivered or services rendered and acts as a formal request for payment.
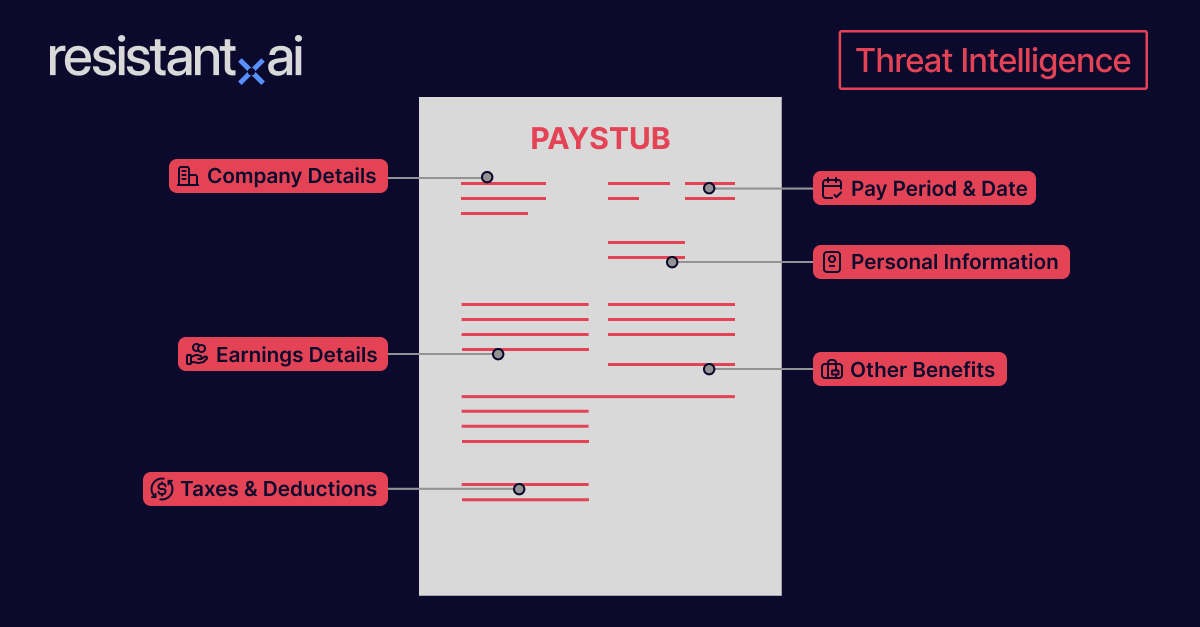
Invoices typically contain:
-
Invoice number
-
Issue date and due date
-
Seller and buyer contact information
-
Description of goods or services provided
-
Quantity, unit price, and total amount
-
Payment terms and methods
-
Applicable taxes or fees
Invoices typically serve as the official proof of a business transaction and are used for accounting and tax purposes.

An example of an invoice for illustrative purposes only
Why are invoices important?
Invoices are usually used to request money from an organization. Their validity needs to be checked to ensure the person is who they say they are and that they deserve the funds they're requesting.
They're also one of the most common documents used to verify and validate business transactions across key processes such as:
-
Accounts payable processing. Finance teams use invoices to match against purchase orders and delivery receipts before releasing payments. This three-way match process helps prevent overpayments, duplicate payments, or fraud.
-
Vendor onboarding. Businesses review sample or previous invoices to verify the legitimacy of new vendors, confirm banking details, and ensure consistency in pricing and services offered.
-
Audit preparation. Invoices are essential supporting documents during internal or external audits, helping companies substantiate expenses and prove regulatory compliance.
-
Expense reimbursement. Employees and departments are often required to submit invoices as part of reimbursement workflows to justify business expenses and maintain clear records for tax purposes.
Invoices are used so widely because they are standardized, traceable, and rich in detail.
They include all the essential information (such as itemized charges, payment terms, contact information, and tax details) and are issued for nearly every commercial transaction, making them a critical document for both operational and compliance-related workflows.
How do fraudsters create fake invoices
Fraudsters primarily commit invoice scams in one of three ways:
-
Modify documents. The most accessible way to create fake invoices is to use online editing tools or PDF editors on a computer to edit the prices or the descriptions of goods and services on existing invoices, and pass them off as real ones.
-
Create fake vendors. Bad actors—especially ones committing internal fraud as happened with this huge Amazon scandal—will sometimes create shell companies through fake invoices, complete with fake contact and payment details in order to embezzle funds.
-
Hacking vendor emails. Commonly known as business email compromise, fraudsters first hack the emails of a vendor or create lookalike email domains, and then send invoices with edited invoice amounts and payment details that reroute funds to their own accounts. This devious tactic has resulted in over $26B in fraud losses for businesses between 2016 to 2019).
-
Buy invoice templates. Bad actors commit invoice fraud by buying and editing pre-made invoice templates. These pre-made invoice templates with modifiable fields are usually found in template farms.
If you’d like to know how fraudsters are creating all these fake invoices, check out our “Types of fraud” blog to learn more about their tactics.
Threat intel: Template data about fake invoices
Our Threat Intelligence Unit collects data about template farms which make and distribute fake document templates for fraudulent purposes.
Below, you'll find an infographic containing data about fake invoice templates, their availability, their distributors, and how much it costs to buy one.

8 Signs of a forged or fake invoice
Accounts payable specialists, procurement managers, and internal auditors who want to check invoices manually must be aware of the common red flags of an invoice scam. Here are some signs to look out for:
1. Data discrepancies
The easiest way to commit invoice fraud is to modify an existing one. However, fraudsters tend to overlook small details and leave discrepancies. Here are some examples to look out for:
-
Mismatched data. Between the purchase order and the invoice itself. This applies to: prices, descriptions, and dates of the goods or services provided.
-
Product description. Does not fit the market price (I.e., a pack of AA batteries that costs 5 times more than what the market sells).
-
Missing information. For example, equipment (such as vehicles) that do not have identification or serial numbers.
-
Invoice number. The purchase order and invoice number are not identical to the documents submitted.
-
Lack of descriptions. On the bills of lading, invoices, and purchase orders.
-
Round number prices. Unlikely without additional information or descriptions of the products or services provided.
2. Changes in contact details
Fraudsters impersonate vendors by using a different email address or compromising a real one. It's crucial to verify contact details in advance, ideally by maintaining a single, reliable point of contact with each vendor.
Another dead giveaway of fraud can be when company logos or payment details on the invoice don’t match previous records.
Whether it's an unusual email address, a mismatched name, or an incorrect account number, any changes in payment information should be carefully verified and approved before funds are released.
3. Irregular invoice submissions
Monitor invoice submissions closely. An unusual spike in the number of invoices from a single vendor may indicate fraudulent activity. Tracking patterns can help identify anomalies that warrant further investigation.
4. Unverifiable vendors
Fraudsters often defraud companies by creating fictitious vendors or 'shell' companies that exist only on paper.
A tell-tale sign of this type of fraud is a sudden change in business relationships, such as replacing a trusted supplier with a new one that has different or suspicious payment details.
Conduct thorough due diligence, including verifying vendor information with procurement teams and using external tools like online searches to confirm the legitimacy of the vendor.
5. Illogical pricing
Illogical pricing on an invoice often manifests in two ways: prices that conflict with historical data or inflated amounts that don't align with market rates.
For instance, if an invoice lists prices seem significantly higher than average, it's essential to cross-check these against historical records to verify authenticity. In the case of inflated prices, apply critical judgment and conduct quick online searches to assess the product's actual market value.
6. Unusual patterns and formats
Every genuine invoice from a firm has the same details when it comes to logos, templates, fonts, paper, billing patterns, etc.
If an invoice deviates from the standard format such as:
It may indicate the possibility of a forged or fake invoice.
7. High-pressure tactics in invoicing
Any invoice that demands urgent payment or the immediate release of funds is usually a red flag.
Typically, payment terms are agreed upon before an invoice is issued, so unexpected urgency is suspicious.
In addition, fraudsters tend to use threatening language such as, “We’ll take legal action if this…” to pressure you into hasty decisions.
Any invoice that emphasizes payment without giving you time for due diligence is likely fraudulent.
8. Lack of documentation
For chemicals, large equipment, and niche products, export and import certifications are usually required.
If an invoice is submitted with vague descriptions, missing serial numbers or certifications, and documentation that is inconsistent with similar products, document verification is critical to weed out bad actors and prevent potential trade finance fraud.
How to verify an invoice?
If you want to successfully spot fake invoices, there are two main methods: manual verification and using AI-powered detection software.
We recommend using a layered AI invoice checker to accelerate the review process and defend against increasingly sophisticated fraud tactics—such as template manipulation, batch-generated forgeries, and supplier impersonation.
Manual inspections carry significant risk, as human reviewers can easily miss subtle discrepancies like altered bank details, mismatched fonts, or cloned layouts.
That said, detecting invoice fraud is a nuanced process, and manual verification still plays an important role. Cross-referencing invoices with purchase orders, delivery receipts, and approved vendor lists is an essential starting point.
However, if you want to reliably prevent invoice fraud at scale (especially in high-volume finance or procurement environments), adopting an AI-driven solution is not optional, it’s necessary.
Manual inspections
The most accessible way to prevent invoice fraud is to manually inspect each document for some of the signs we detailed above.
Experienced employees must rely on a keen eye for detail, instincts, strong record-keeping, and the list of red flags we mentioned above.
Keep in mind: As fraud techniques become ever more sophisticated and technologically advanced, manual inspections to prevent document fraud are inevitably limited, both in terms of effective detection and the business delays they can cause.
Using AI and machine learning software to spot fake invoices
AI document fraud detection services analyze digital documents in seconds to uncover signs of modification and tampering.
This gives risk, underwriting, and audit teams instant confirmation of document authenticity or forgery, letting them focus their investigative resources effectively and speeding up their approval or rejection processes.
Conclusion
Invoice fraud is a growing threat, and traditional methods alone aren't enough to keep up with the evolving tactics used by bad actors.
While manual checks offer a basic level of defense, they simply can't match the speed, scale, or precision of AI-powered verification.
To truly protect your organization and maintain trust in your financial workflows, it's time to adopt smarter tools.
Scroll down and book a demo to see our document verification solution in action—and discover how we help businesses stay one step ahead of fraud.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Hungry for more fake invoice content? Here are some frequently asked questions from around the web about how to spot fake invoices.
What to look for in an AI-driven document fraud detector?
AI and machine learning greatly enhance a company’s document verification processes by improving precision and accuracy in detecting fake invoices—with low false positives. Here are five essential components that a good AI document fraud detection software should have:
-
High accuracy. An AI-powered document fraud detector must verify invoices with a high level of accuracy to give credit companies, trade financiers, and merchants the confidence to process large volumes swiftly. This includes identifying subtle signs of forgery, fake templates, and other fraud indicators that are often undetectable to the human eye, ensuring that fraudulent invoices don’t slip through document verification processes.
-
Support for multiple document formats. An AI document fraud detection software that analyzes different document formats like PDF, JPEG, and PNG facilitates smoother document verification processes by giving customers more options to submit invoices.
-
Clear verdicts. A high-quality AI document fraud detector should provide clear verdicts that do not need further interpretation—enabling you to approve or deny invoices based on clear, evidence-backed results to minimize potential risks.
-
Explainable results. Explainable results enable credit companies, trade financiers, and merchants to understand the risk each invoice carries, helping them assess its authenticity and verify an applicant’s income.
-
Configurable to match your risk appetite. The best AI document fraud detector can be configured by businesses to detect outcomes with their risk appetite—only accepting or approving invoices that only come in certain formats, for example.
What's the difference between an invoice, purchase order, and bill of lading?
These documents are frequently used together in business transactions but serve very different purposes. Each represents a distinct stage in the buying and shipping process, and understanding their roles is key to verifying legitimacy and preventing fraud.
Invoice: A formal request for payment issued by a seller to a buyer after goods or services have been delivered.
-
Issued by:
-
Characteristics:
-
Includes item descriptions, pricing, totals, due dates, and payment terms
-
Used for accounting, payment processing, and audit trails
-
Critical for expense tracking and financial documentation
Purchase Order (PO): A buyer-generated document authorizing a purchase and outlining the specifics of the order before delivery or invoicing.
-
Issued by:
-
Characteristics:
-
Includes item quantities, pricing, delivery timelines, and PO number
-
Used to authorize spending and establish contractual terms
-
Helps match and verify invoices and shipments during fulfillment
Bill of Lading (BOL): A legal document issued by a carrier confirming receipt of goods for shipment and outlining the delivery terms.
-
Issued by:
-
Characteristics:
-
Acts as a receipt, contract of carriage, and document of title
-
Lists goods being transported, their destination, and consignee
-
Essential for customs clearance, insurance claims, and shipment tracking
Is there a software to detect fake invoices?
Yes, there are advanced software solutions designed to detect fake invoices using AI and machine learning. These tools analyze document structure, data consistency, metadata, and cross-reference records to flag suspicious entries.
Resistant AI offers a purpose-built document verification solution that helps businesses verify invoices at scale and protect against invoice fraud.
Is making fake invoices illegal?
Yes, creating or using fake invoices is considered a form of fraud and is illegal in most countries. It can lead to criminal charges, financial penalties, and civil lawsuits depending on the severity and intent of the deception.
Who needs to check fake invoices?
Several roles across finance and operations are responsible for detecting fake invoices to prevent fraud, ensure compliance, and protect company funds:
-
Accounts payable specialists. They review and process invoices before payment, making them the first line of defense against overbilling, duplicates, or forged documents.
-
Procurement managers: They verify that invoices align with purchase orders and delivery confirmations to ensure the business only pays for goods or services actually received.
-
Internal auditors. They examine invoices during audits to detect anomalies, validate controls, and ensure adherence to financial regulations.
-
Compliance officers. They monitor invoice authenticity as part of broader anti-fraud and anti-money laundering (AML) policies, especially in regulated industries.